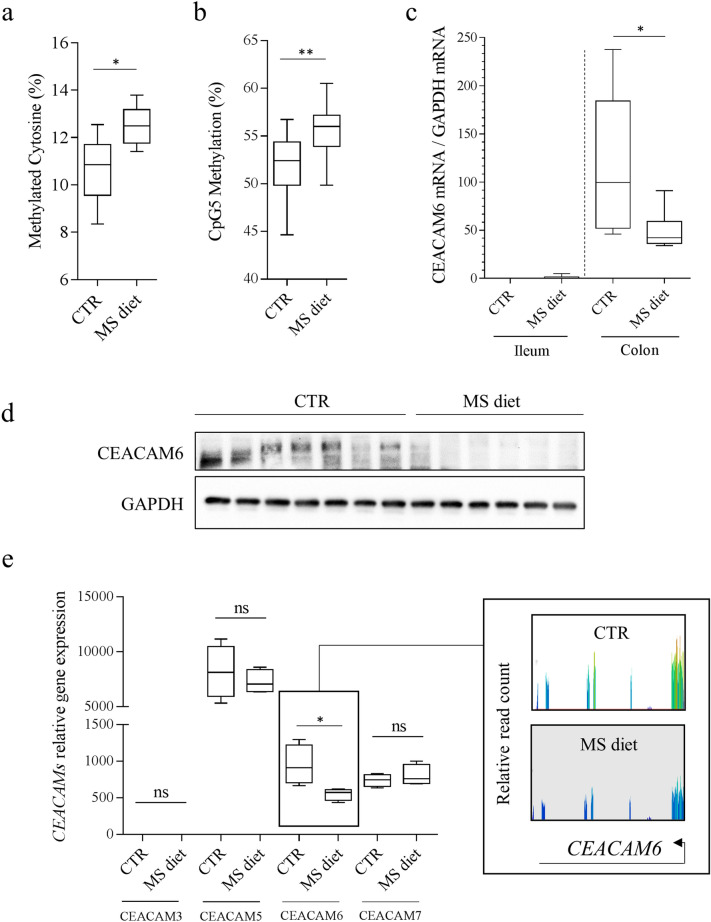
Figure 1.
Methyl-donor supplementation decreases CEACAM6 expression through hypermethylation of its promoter in intestinal epithelial cells in vivo. (a) Cytosine methylation levels on LINE elements from colonic mucosa of mice fed a control (CTR) or Methyl-Supplemented diet (MS diet). (b) Methylation level of CpG5 (within HIF-1 responsive element) within CEACAM6 promoter was measured on purified enterocytes from mice fed a control diet (CTR) (n = 12) and MS diet (n = 10) using Bisulfite-SnapShot. (c) CEACAM6 mRNA was quantified by RT-qPCR in ileal and colonic mucosa (n = 4). (d) Western blot performed on colonic mucosa of CEABAC10 mice fed a CTR or MS diet for quantification of CEACAM6 expression (n = 7 and 6 respectively). The two signals were obtained from the same gel migration. The membrane was cropped as the anti-CEACAM6 antibody was made in mice; hence the secondary antibody recognizes the heavy and light chains of endogenous IgG, masking the CEACAM6 signal. Uncropped membranes are shown in Supplementary Figure S1. (e) CEACAMs genes expression encoded by the CEABAC transgene was measured in colonic mucosa from mice fed a control diet (CTR) (n = 4 biological replicates) and MS diet (n = 4 biological replicates) by RNA-seq. Insert: Screen-shot of quantified CEACAM6 reads from RNA-seq data. Mann–Whitney test. ns non-significant. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.