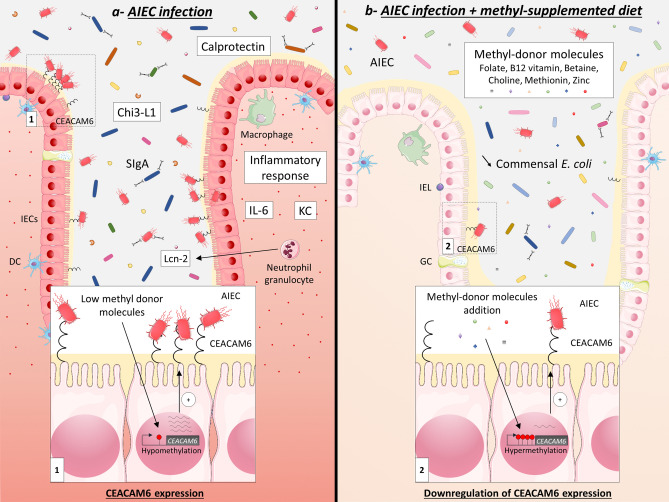
Figure 6.
Methyl-donor supplementation in the diet prevents intestinal colonization by AIEC pathobiont. (a) In CEABAC10 mice fed a conventional diet, CEACAM6 promoter is hypomethylated in IECs, which leads to a high expression of CEACAM6 (insert 1) and, as a consequence, to a great ability of AIEC bacteria to colonize the intestinal mucosa and to induce a pro-inflammatory response (IL-6, KC, Chi3-L1, Calprotectin and Lcn-2). Numerous bacteria are also coated by SIgA in this specific context. (b) In CEABAC10 mice fed a methyl-donor-supplemented diet, CEACAM6 gene promoter is hypermethylated in IECs, which leads to a decrease in its expression level (insert 2) and, as a consequence, to a lower intestinal colonization of the mucosa by AIEC bacteria and to a controlled inflammatory response. Of note, the load of commensal Enterobacteria is profoundly affected by the diet, which is associated to a lower IgA secretion in the lumen. Chi3-L1 Chitinase 3-Like 1, DC dendritic cells, GC goblet cells, IECs intestinal epithelial cells, IEL intraepithelial lymphocytes, IL-6 interleukin 6, KC keratinocyte chemoattractant, Lcn-2 Lipocalin-2, SIgA Secretory Immunoglobulin A. This figure was created using Servier Medical Art templates, which are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License; https://smart.servier.com.