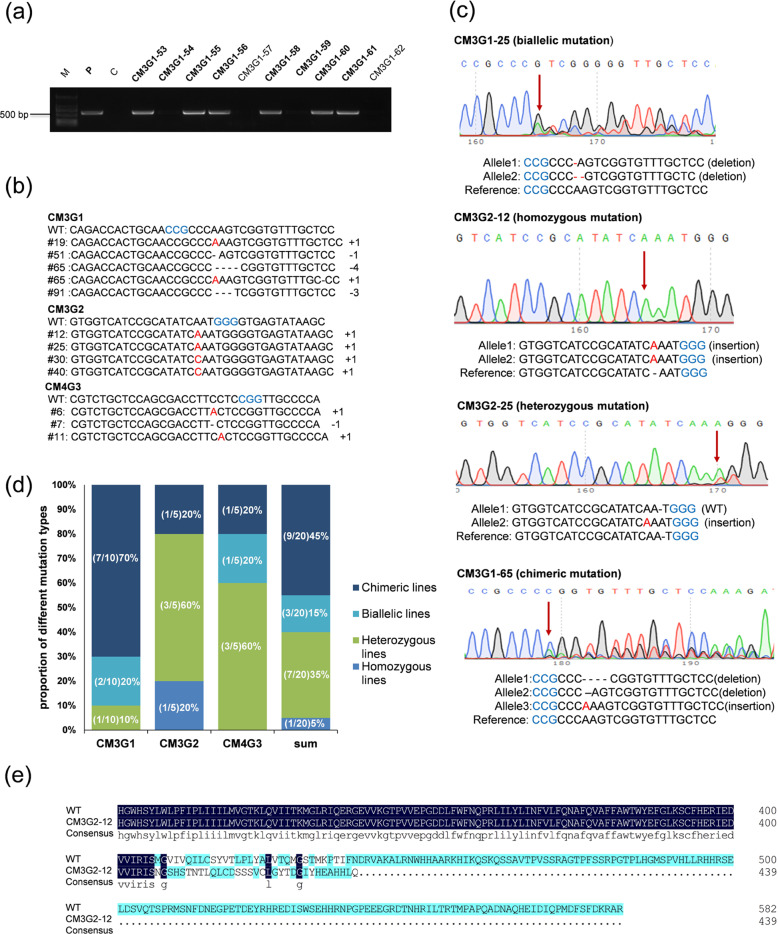
Fig. 3. Targeted mutagenesis of VvMLO3 and VvMLO4 using the CRISPR-Cas9 system.
a PCR amplification of a 507-bp DNA fragment of genomic DNA from regenerated plantlets using gene-specific primers. M: marker, P: plasmid, C: control, CM3G1-53 to CM3G1-62: different regenerated lines expressing VvMLO3-sgRNA1. b The numbers on the right indicate the type of mutation and the number of nucleotides involved, “−” and “+” indicate deletions and insertions, respectively. The insertions are highlighted in red letters, and the protospacer-adjacent motif (PAM) is indicated in blue letters. c Four different types of mutation sequencing chromatograms: biallelic, homozygous, heterozygous, and chimeric mutations. The first substitution or indel sites are indicated with red arrowheads. The protospacer-adjacent motif (PAM) sequences are highlighted in blue, the indels or substituted bases are highlighted in red, and ‘−’ indicates deletions. d The frequency of different mutation types found in the edited lines. e Amino acid sequence alignment between one representative mutant and the wild-type for the target region of VvMLO3.