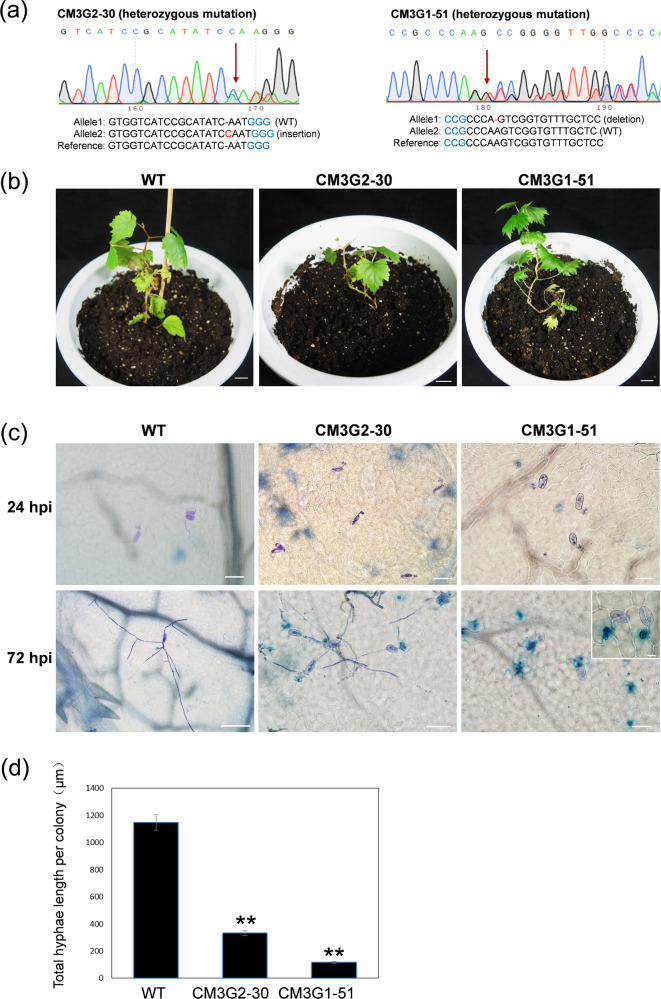
Fig. 5. Different types of mutations confer different levels of resistance.
a Sequence chromatograms of mutation lines CM3G2-30 and CM3G1-51. The first substitution or indel sites are indicated with red arrowheads. The protospacer-adjacent motif (PAM) sequences are highlighted in blue, and the indels or substituted bases are highlighted in red. ‘−’ indicates deletions. b Comparison of the wild-type (WT) and different types of VvMLO3-edited lines 15 days after transplantation from subculture medium. c Representative micrographs showing the growth of powdery mildew in the WT and VvMLO3-edited lines at 24 and 72 hpi. Bars = 100 μm except for that (20 μm) in the inset. d Total hyphal length per powdery mildew colony on the leaves of the VvMLO3-edited lines and WT inoculated with En NAFU1 at 72 hpi. Data are the means ± SE calculated from three replicate experiments. Asterisks indicate significant differences between the edited lines and the Thompson Seedless WT control (P < 0.01; n = 3, Student’s t test).