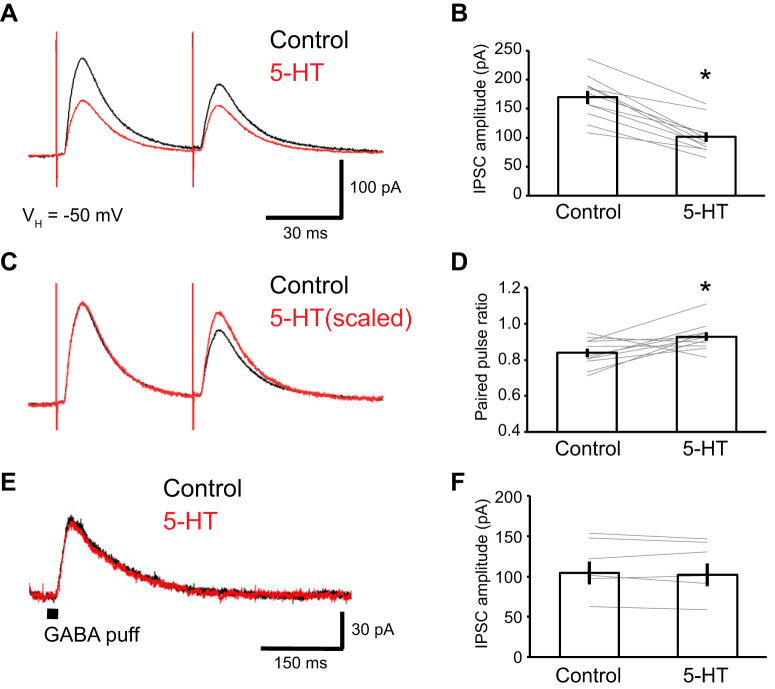
Fig. 3.
Presynaptic origin of the suppression of GABAA inhibitory postsynaptic currents (IPSCs) by 5-HT. The GABAA IPSCs were isolated with CNQX (10 µM), dl-APV (50 µM), and CGP55845 (1 µM). A: representative traces of paired-pulse IPSCs in the absence (black) and presence (red) of 5-HT. B: amplitude of the first IPSC induced by paired-pulse stimulation in control conditions and in the presence of 5-HT (from 170.0 ± 11.3 to 101.0 ± 8.7 pA; paired t test; df = 10; t = 8.69; P < 0.001; n = 11). The extent of suppression was much the same as for the single pulse IPSCs. C: scaled traces for comparing the paired-pulse ratio. D: paired-pulse-ratio in 11 tested neurons, in the absence (black) or presence (red) of 5-HT. The paired-pulse ratio was significantly increased by 5-HT (IPSC2/IPSC1; from 0.84 ± 0.02 to 0.93 ± 0.02; paired t test; df = 10; t = −2.58; P = 0.027; n = 11). E: representative traces of GABAA current induced by a direct GABA (50 µM) puff to the recorded neuron. F: amplitude of GABAA current induced by direct GABA puff applications in 6 tested neurons (from 114.2 ± 14.0 to 111.7 ± 14.03 pA, paired t test; df = 5; t = 0.85; P = 0.431, n = 6). *P < 0.05.