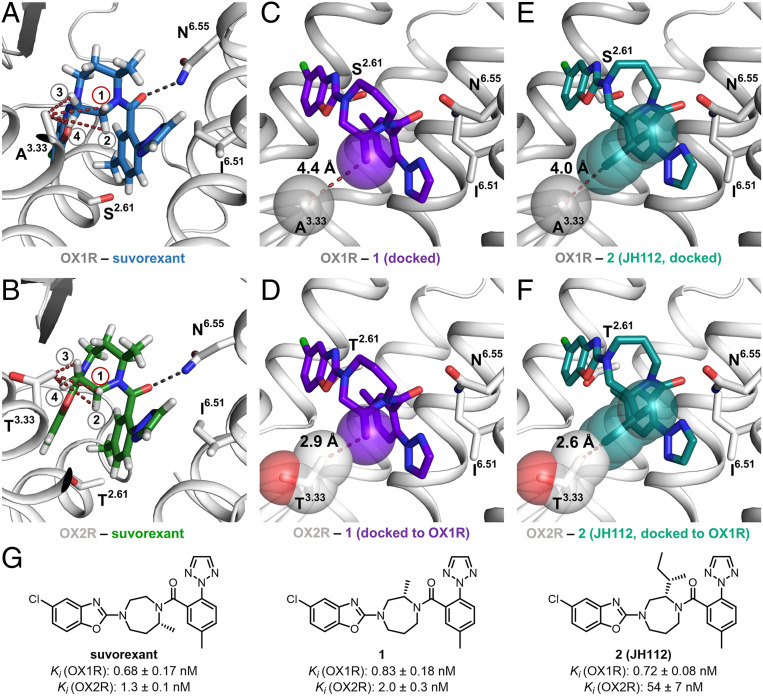
Fig. 1.
Comparison of the orthosteric binding sites of OX1R and OX2R and development of compound 2 (JH112). (A and B) The orthosteric binding pocket of OX1R and OX2R with conserved features of ligand recognition and binding affinities of the cocrystallized ligand suvorexant (hydrogens displayed). The only nonconserved residues in the two binding pockets are located in TM2 (OX1R: Ser2.61; OX2R: Thr2.61) and TM3 (OX1R: Ala3.33; OX2R: Thr3.33). (A) Distances between hydrogen 1 to 4 and the carbon of the Ala3.33 side chain: H1: 4.4 Å; H2: 5.3 Å; H3: 3.9 Å; H4: 4.3 Å. (B) Distances between hydrogen 1 to 4 and the terminal carbon of the Thr3.33 side chain: H1: 3.4 Å; H2: 4.5 Å; H3: 3.0 Å; H4: 3.2 Å. (C) Docking pose of compound 1 indicating that a methyl substituent in position H1 of the suvorexant points toward the nonconserved Ala3.33 of the OX1R. Distance between the carbon of the methyl substituent and Cβ of the Ala3.33 side chain: 4.4 Å. (D) Alignment of OX2R to OX1R with docked compound 1 in the binding pocket, indicating a steric clash between the methyl substituent of compound 1 and the nonconserved Thr3.33 of the OX2R. Distance between methyl substituent and Thr3.33: 2.9 Å. (E) Docking pose of compound JH112 indicating that the sec-butyl substituent fits into OX1R’s binding site (minimum distance between the sec-butyl substituent and Ala3.33 side chain: 4.0 Å). Compound JH112 adopts a similar binding conformation as suvorexant. (F) Alignment of OX2R to OX1R with docked compound JH112 in the binding pocket indicating a steric clash between the sec-butyl substituent of JH112 and the nonconserved Thr3.33 of OX2R. Minimum distance between sec-butyl substituent and Thr3.33: 2.6 Å. (G) Chemical structures of the compounds and binding affinity.