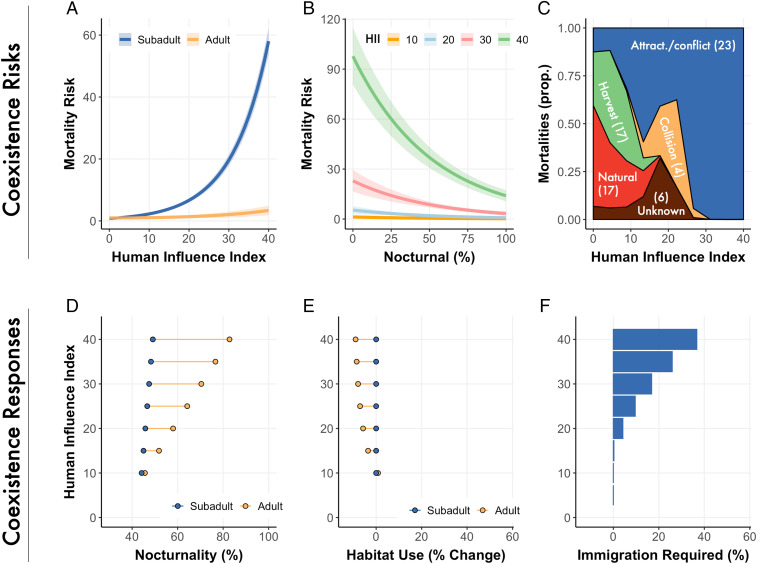
Fig. 2.
Per capita risk of annual mortality predicted from Cox proportional hazard model for subadult (3 to 6 y old) and adult (>6 y old) bears across HII gradients (A) and for HII and nocturnality (B). See SI Appendix, Section 2.2 for further details on hazard models. Uncertainty shown as SE. (C) Proportion of mortalities by cause by HII for animals > 2 y old; 76% of recorded mortalities were human-caused. Number of observed mortalities by cause is shown in brackets. Attract./conflict = mortality due to an attractant or conflict issue. Relationship between HII and (D) nocturnality (percent) between age classes, and (E) change in habitat use between age classes, indicating the degree to which animals changes their use of HII as they aged. For example, where HII = 20, this shows the change in habitat use as animals moved from subadults to adults when the area used by the subadult had an average HII area of 20, and (F) immigration required (percent of population) to sustain stable brown bear populations (population growth = 1).