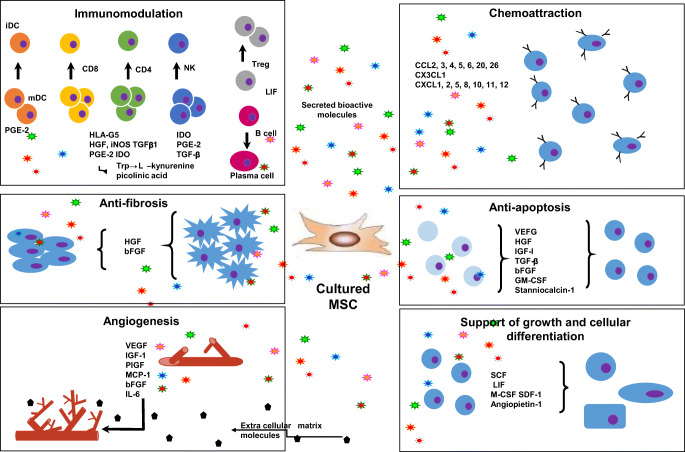
Fig. 1.
MSCs, in general, accelerate healing processes by acting at the level of immunomodulation, antiapoptosis, angiogenesis, supporting the growth and differentiation of local stem and progenitor cells, antiscarring, and chemoattraction. BFGF - basic fibroblast growth factor; CCL - CC chemokine ligand; CXCL - chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand; ECM - extracellular matrix; GM-CSF - granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; HGF - hepatocyte growth factor; iDC - invasive ductal carcinoma; IGF-1 - insulin growth factor-1; LIF - leukaemia-inhibitory factor; M-CSF - macrophage colony-stimulating factor; mDC - macrophage-derived chemokine; NK - natural killer cells; PGE2 - prostaglandin E2; SCF - stem cell factor; SDF-1 - stromal cell-derived factor 1; TGF-β - transforming growth factor-β; VEGF - vascular endothelial growth factor [42]