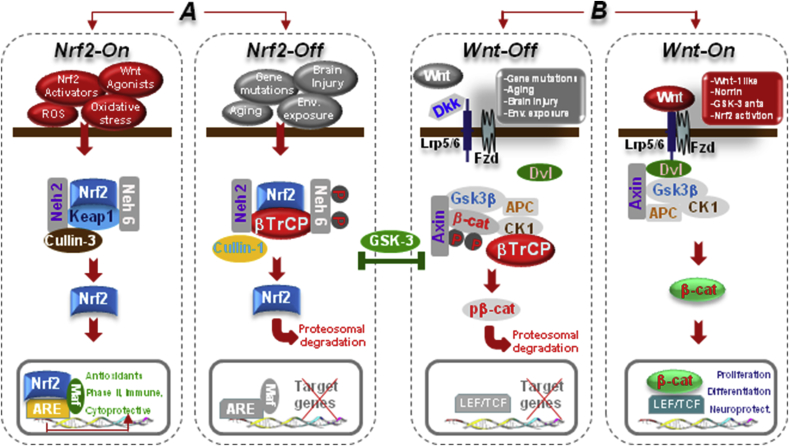
Fig. 2.
The Nrf2-ARE and Wnt/β-catenin/GSK-3β intertwined signaling cascades. A. In normal conditions, Nrf2 is inactive (Nrf2-Off”) and resides in the cytoplasm bound to Keap1. In response to oxidative stress and inflammation, the modification of Keap1 cysteine residues leads to inhibition of Nrf2 ubiquitylation and stabilization of Nrf2, allowing Nrf2 to accumulate in the cytosol and then to translocate into the nucleus where it binds to a small Maf protein and activates transcription of genes containing antioxidant response elements (AREs) in their regulatory regions (Nrf2-On”) [[76], [77], [78]]. In addition to its interaction with Nrf2, Keap1 also binds Cullin 3 (Cul3), which forms a core E3 ubiquitin ligase complex through an association with Ring-box1 protein (Rbx1, also called Roc1) [[76], [77], [78]]. Besides Keap1-mediated regulation, two other E3 ubiquitin ligases have been found to regulate the protein level of Nrf2. Nrf2 is controlled by two distinct β-TrCP recognition motifs in its Neh6 domain, one of which can be modulated by glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK-3β) activity phosphorylating a group of Ser residues in the Neh6 domain of Nrf2 [81, 82, see text]. B. In Wnt/β-catenin pathway, Wnt signal activation is tightly controlled by a dynamic signaling complex, constituted by class Frizzled (Fzd) of the G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCRs) superfamily, the LDL receptor-related protein (LRP) 5/6 coreceptors and Dishevelled (Dvl) and Axin adapters [75]. In the absence of a Wnt ligand, (Wnt-off) the signaling cascade is inhibited. Cytoplasmic β-catenin is phosphorylated and degraded via proteasome mediated destruction, which is controlled by the “destruction complex”, consisting of GSK3β, casein kinase 1α (CK1α), the scaffold protein AXIN, and the tumor suppressor adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) [75]. As a result, the translocation into nucleus is inhibited. Interruption of Wnt/β-catenin signaling also occurs in the presence of the Dkk’ and secreted FZD-related proteins (sFRPs) families of Wnt-antagonists, or Wnt inhibitory protein, WIF. Conversely, Wnt ligand binding to Fzd receptors at the surface of target cells (Wnt-on) triggers a chain of events aimed at disrupting the degradation complex via Dvl phosphorylation [75]. Then β-catenin is separated from the destruction complex, resulting in its accumulation and stabilization in the cytoplasm. Subsequently, β-catenin is imported into the nucleus where it can interact with the TCF/LEF family of transcription factors and recruit transcriptional co-activators, p300 and/or CBP (CREB-binding protein), as well as other components to transcribe a panel of downstream target genes. Conditions that can direct to Nrf2/Wnt-On (Nrf2-activators, GSK-3-antagonists, Wnt1-agonists.) or to Nrf2/Wnt-/Off (PD gene mutations, ageing, inflammation, environmental toxins.) are indicated. Because GSK-3β crosstalk with both Nrf-ARE and canonical Wnt-signaling, inhibition of GSK-3β activity by molecular compounds and various enzymes represents a potential means to activate the anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory, prosurvial, neuroprotective and neurogenic downstream Nrf2/Wnt gene cascades (for details, see the text).