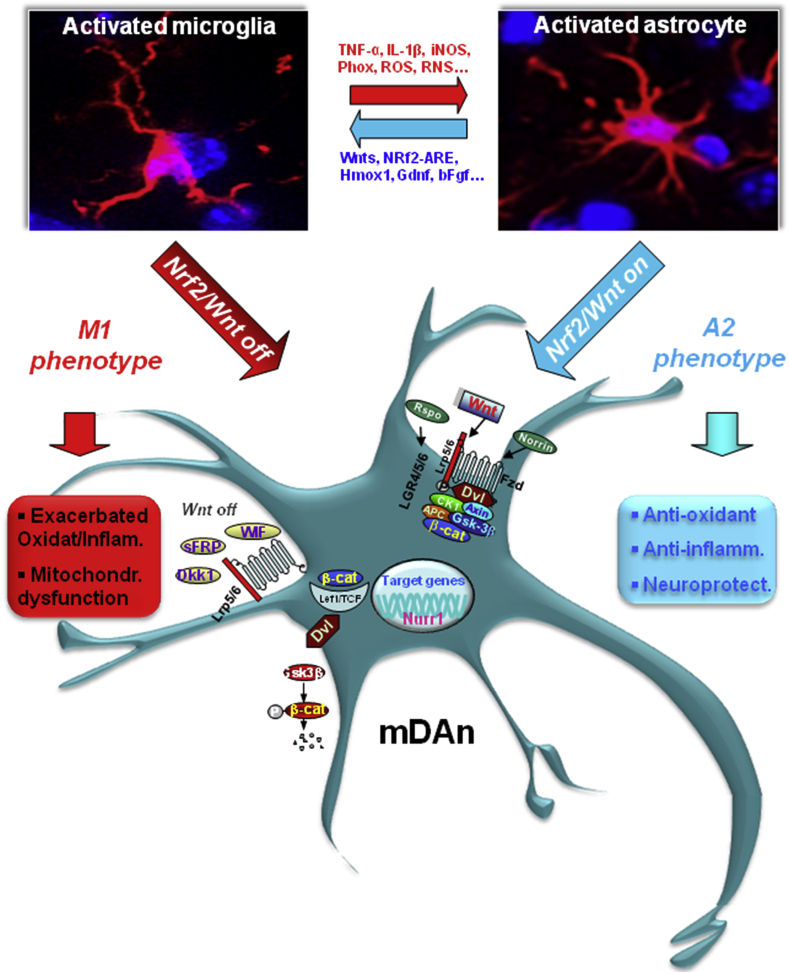
Fig. 7.
Astrocyte-microglia interactions and Nf2/Wnt1/β-catenin resilience in mDAn neuroprotection. Major environmental factors including ageing, inflammation, neurotoxin exposure (MPTP/MPP+, 6-OHDA, pesticides), in synergy with genetic mutations results in dysfunctional astrocyte-microglial crosstalk associated to the exacerbated production of proinflammatory mediators. The glial switch to the A1/M1 harmful astrocyte and microglial phenotype is the result of the inhibition of Nrf2/Wnt/β-catenin signaling (“Nrf2/Wnt off”). In these conditions, reactive astrocytes no longer mount an efficient resilience program for the vulnerable mDAns. Hence, the crucial anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory Nrf2/HO-1 and dopaminotrophic factors, namely Wnt1, are sharply inhibited. As a result, active GSK-3β is up-regulated in mDAns, leading to β-catenin degradation. Then, in the absence of an efficient Nrf2-ARE axis at play, the “frailty” of mDAns increases in turn leading to mDAn degeneration. By contrast, astrocyte upregulation of Nrf2/HO-1 and Wnt1/β-catenin during oxidative stress and inflammation represent a critical resilience program for DAns. Then, increased astrocyte-derived Wnt1 (and Wnt1-like agonists, such as Wnt1, Rspo or Norrin) activates Fzd-1 receptors (“Wnt on”), leading to the blockade of GSK-3β-induced phosphorylation (P) and proteosomal degradation of the neuronal pool of β-catenin. Stabilized β-catenin can translocate into the nucleus and associate with a family of transcription factors and regulate the expression of Wnt target genes involved in DA neuron survival/plasticity, neuroprotection and repair. β-catenin may also function as a pivotal defense molecule against oxidative stress, and can act as a coactivator for several nuclear receptors involved in the maintenance/protection of DA neurons. The hypothetical contribution of various endogenous Wnt agonists (Responding, Rspo, Norrin) or antagonists (Dkkopf, Dkk1, Wif, frizzled-related proteins, SFRp) are also indicated. Resilience of Nrf2/Wnt/β-catenin program can be activated by several treatments, including GSK-3β antagonists, Wnt1-like agonists, nitric-oxide–(NO)–anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs (NSAID). Different conditions/treatments can inhibit Nrf2/Wnt beneficial signaling cascades, including gene mutations, ageing, inflammation, endogenous Wnt-antagonist expression, leading mDAn degeneration (see the text for details).