Fig. 2.
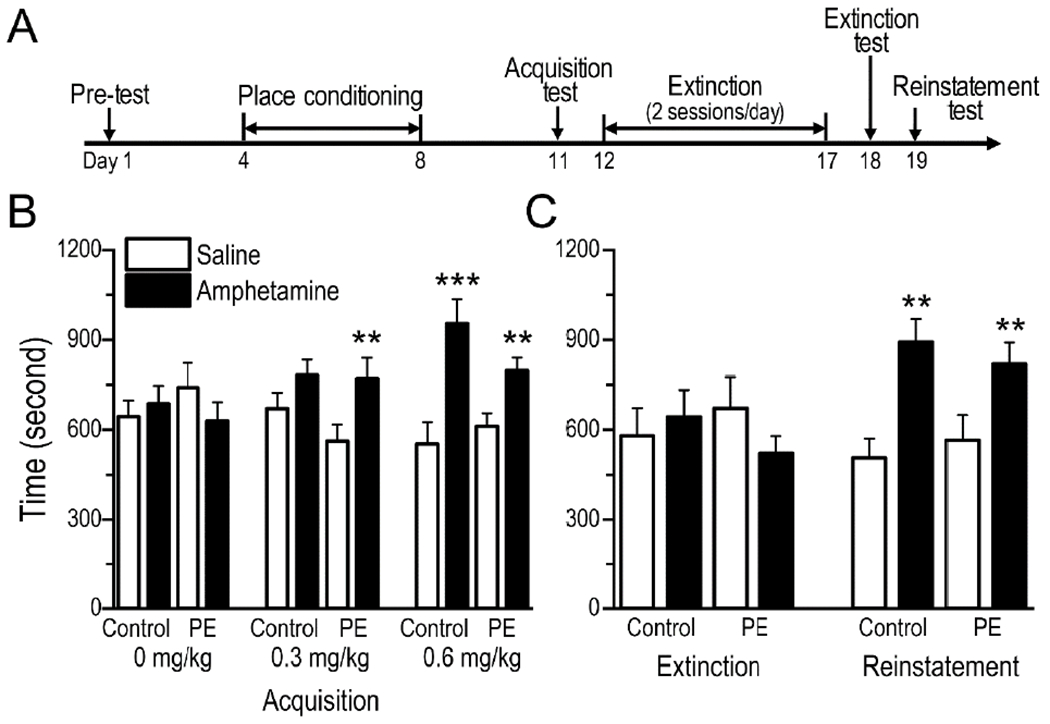
Prenatal ethanol exposure (PE) facilitated acquisition of amphetamine-induced conditioned place preference (CPP). (A) Timeline of the amphetamine CPP experiments. (B) Amphetamine CPP was observed in PE but not control rats at the 0.3 mg/kg (i.p.) dose. In contrast, CPP was observed in both groups at the 0.6 mg/kg (i.p.) dose. The uneven pairings of saline and amphetamine did not influence the results, because 0 mg/kg amphetamine (i.p.) did not induce CPP in either group. (C) Extinction training eliminated CPP in both PE and control rats conditioned with amphetamine at 0.6 mg/kg. In addition, 0.3 mg/kg amphetamine (i.p.) reinstated CPP in both control and PE rats. No group differences were observed in either extinction or reinstatement of CPP. Data are presented as Mean ± SEM, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001, time spent in amphetamine- vs. saline-paired compartment in control or PE rats within 30 min, planned comparisons after ANOVA.
