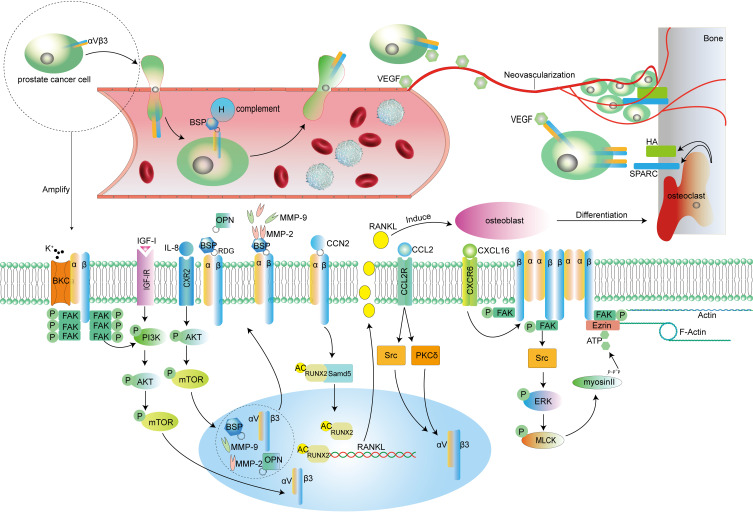
Figure 1.
The figure describes the process by which αVβ3 mediates prostate cancer cell metastasis. Macroscopically, after cancer cells destroy the ECM and leave their primary site, cancer cells depend on αVβ3, which destroys vascular endothelial cells, to enter blood vessels. In blood vessels, tumor cells under the protection of BSP escape the attack of the immune system and then pass through the blood vessels to reach the metastatic site. Here, bone tissue is used as an example. Under the induction of VEGF, cancer cells recognize SPARC and HA and interact with them on the surface of bone with the help of αVβ3; at the same time, VEGF induces neovascularization to supply blood to the cell mass system. At the microscopic level, IL-8, IGF-I, CCN2 and other ligands activate different signaling pathways to promote the expression of αVβ3 in cancer cells. In addition, CCN2 transmits signals into the cell through αVβ3 to increase the acetylation of the transcription factor RUNX2, and RUNX2 promotes RANKL expression in tumor cells; these tumor cells then secrete RANKL to induce osteoblast differentiation into osteoclasts, and osteoclast-mediated bone tissue remodeling can expose HA and SPARC on the bone surface. BKCa and CXCL16 promote the aggregation and activation of αVβ3 and trigger the activation of downstream FAK. In addition to enhancing the activity of the ERK or PI3K pathway, activated FAK triggers cytoskeletal protein remodeling with the help of adaptor proteins, further enhancing tumor cell invasion ability. Cell information: The PC-3 cell line was initiated from the bone metastasis of a grade IV prostatic adenocarcinoma from a 62-year-old Caucasian male; DU145 was initiated from a 69-year-old Caucasian male with brain metastasis of prostatic adenocarcinoma; LNCAP was isolated from the left supraclavicular lymph node of a 50-year-old prostate cancer patient. LNCAP is sensitive to hormones; C4-2B is a subtype derived from the LNCAP cell line.
Abbreviations: BSP, bone sialoprotein; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; HA, hydroxyapatite; SPARC, osteonectin; FAK, focal adhesion kinase; IGF-I, insulin-like growth factor; IL-8, interleukin8; OPN, osteopontin; MMP (2 or 9), matrix metalloproteinase (2 or 9); CCN2, connective tissue growth factor; CCL2, chemokines2; CXCL16, chemokines16; P, phosphorylated; AC, acetylated.