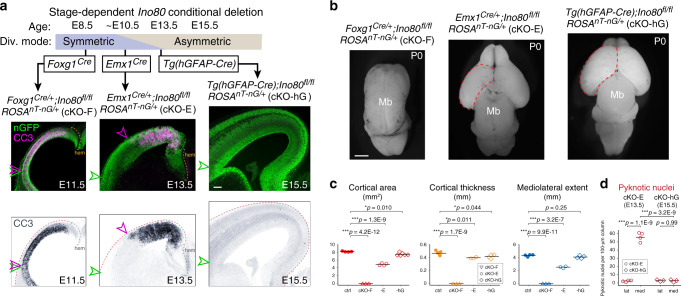
Fig. 7. Systematic deletion of Ino80 from NPCs pre-, peri-, and post transition to asymmetric division.
a Ino80 was systematically deleted from NPCs pre-, peri-, and post transition from symmetric to asymmetric division (Div.). Cre-dependent nGFP reporter (green) was expressed from ROSAnT-nG. Foxg1Cre deletion of Ino80 (cKO-F) during exclusively symmetric NPC–NPC divisions led to widespread CC3 staining (magenta in overlay, blue in monochrome) throughout the mediolateral axis of E11.5 cortex. The lateral extent of apoptosis (magenta arrowhead) reached the lateral extent of the neocortex (green arrowhead). Emx1Cre deletion of Ino80 (cKO-E) near the onset of transition between symmetric and asymmetric divisions led to robust apoptosis in medial, but not lateral, neocortex. Tg(hGFAP-Cre) deletion of Ino80 (cKO-hG) after most NPCs transitioned to asymmetric neurogenic division did not lead to an increase in apoptosis (n = 3 animals). b Dorsal view of P0 whole-mount brains. cKO-F was characterized by forebrain agenesis. cKO-E exhibited microcephaly and medial defects in corticogenesis. cKO-hG brains were similar to ctrl in size and morphology (cKO-F: n = 3, cKO-E: n = 4, cKO-hG: n = 6). c Cortical area (red), thickness (yellow), and mediolateral extent (blue) of P0 cKO-F, cKO-E, and cKO-hG compared with ctrl (data are mean, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test, ctrl: n = 4, cKO-F: n = 3, cKO-E cortical area: n = 4, cKO-E thickness and mediolateral extent: n = 3, cKO-hG cortical area: n = 6, cKO-hG thickness and mediolateral extent: n = 4 animals). d Pyknosis was significantly increased in medial E13.5 cKO-E cortex, but not in E15.5 cKO-hG cortex (data are mean, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test, cKO-E: n = 4, cKO-hG: n = 3 animals). Scale bar: 100 μm in a; 1 mm in b.