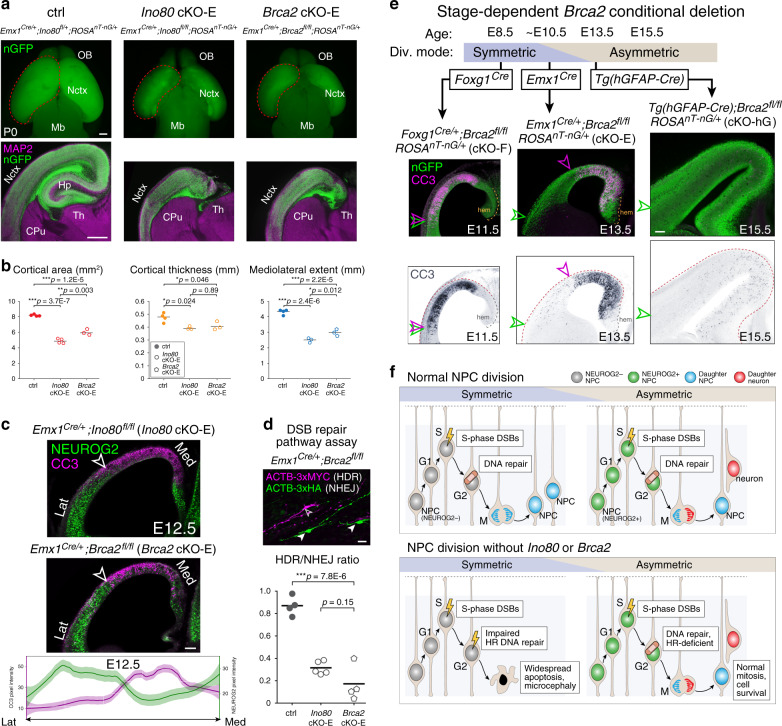
Fig. 8. A selective requirement for Ino80-mediated HR in symmetric NPC–NPC divisions.
a P0 whole-mount brains and immunostaining for MAP2 (magenta) and nGFP (green). Emx1Cre-mediated deletion of HR gene Brca2 (Brca2 cKO-E) led to microcephaly and hippocampal hypoplasia reminiscent of Ino80 cKO-E (n = 3 animals). b The significant reductions in Ino80 cKO-E cortical area (red), thickness (yellow), and mediolateral extent (blue) were each phenocopied in Brca2 cKO-E (data are mean, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test, ctrl: n = 4, Ino80 cKO-E cortical area: n = 4, thickness, mediolateral extent: n = 3, Brca2 cKO-E: n = 3 animals). c Complementary gradients of asymmetric neurogenic divisions (NEUROG2, green) and apoptosis (CC3, magenta) in Brca2 cKO-E E12.5 cortex similar to those found in Ino80 cKO-E (data are LOESS curve ± 99% confidence interval, n = 3 animals). d In vivo DSB repair pathway assay revealed significant decrease in HDR (ACTB-3xMYC, magenta) relative to NHEJ (ACTB-3xHA, green) in Brca2 cKO-E compared with ctrl (data are mean, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test, ctrl: n = 4, Ino80 cKO-E: n = 5, Brca2 cKO-E: n = 4 animals). e Foxg1Cre deletion of Brca2 (cKO-F) during exclusively symmetric NPC–NPC divisions led to widespread CC3 (magenta in overlay, blue in monochrome) throughout the mediolateral axis of E11.5 cortex. The lateral extent of apoptosis (magenta arrowhead) reached the lateral extent of neocortex (green arrowhead). Emx1Cre deletion of Brca2 (cKO-E) near the onset of transition between symmetric and asymmetric divisions led to robust apoptosis in medial, but not lateral, neocortex. Tg(hGFAP-Cre) deletion of Brca2 (cKO-hG) after most NPCs had transitioned to asymmetric neurogenic division did not lead to widespread increase in apoptosis. These Cre-by-Cre phenotypes were reminiscent of those found in Ino80 cKOs (n = 3 animals). f During corticogenesis, synthesis-associated DSBs in dividing NPCs are repaired in S, G2, or M phase to safeguard genome integrity. Following Ino80 or Brca2 deletion from NPCs, HR was selectively disrupted. In symmetrically dividing NPCs, loss of HR led to unrepaired DSBs and apoptosis. In asymmetrically dividing NPCs, Ino80 or Brca2 deletion did not give rise to unrepaired DSBs or apoptosis, suggesting that homology-independent DNA repair pathways were sufficient. Thus, distinct modes of NPC division have divergent requirements for HR DNA repair. Scale bar: 500 μm in a; 100 μm in c, e; 20 μm in d.