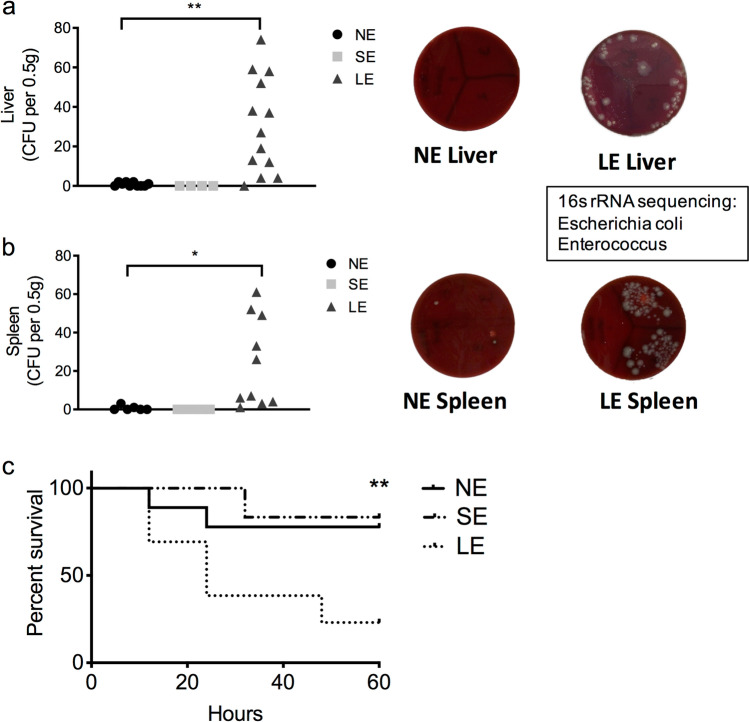
Figure 2.
LE mice had baseline bacterial translocation to the liver and spleen and increased susceptibility to K. pneumoniae sepsis. (a) Baseline cultures from the liver of NE, SE and LE mice showing number of colonies grown on aerobic blood agar culture and representative culture plates from NE and LE mice. (b) Baseline cultures from the spleen of NE, SE and LE mice showing number of colonies grown on aerobic blood agar culture and representative culture plates on NE and LE mice. Anaerobic cultures did not grow any colonies (data not shown). Only the LE group had increased numbers of bacterial colonies. 16s rRNA sequencing of colonies grown from LE mice identified them as Escherichia coli and Enterococcus. (c) Kaplan–Meier survival graph of NE, SE and LE mice exposed to K. pneumoniae induced sepsis. Compared to the other groups, LE mice had significantly increased mortality. Data shown are representative of 4 experiments with 9–14 mice in each group. Statistical analysis used were ANOVA (a,b) and log-rank (c). Data are depicted as mean ± SEM (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01).