Fig. 2. Schematic showing an overview of nerve regeneration after injury induced by the dedifferentiation of Schwann cells.
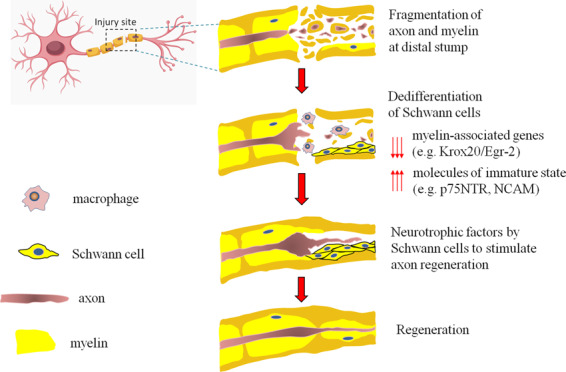
The fragmentation of axons and myelin occurs at the injury site. The mature myelinating Schwann cells dedifferentiate, regain the expression pattern associated with immature Schwann cells and proliferate. Then, Schwann cells remove myelin and axonal debris after dedifferentiation by themselves or by recruiting circulating macrophages and produce neurotrophic factors to support axon regeneration.
