Figure 2. Suppression signals of ILC3s.
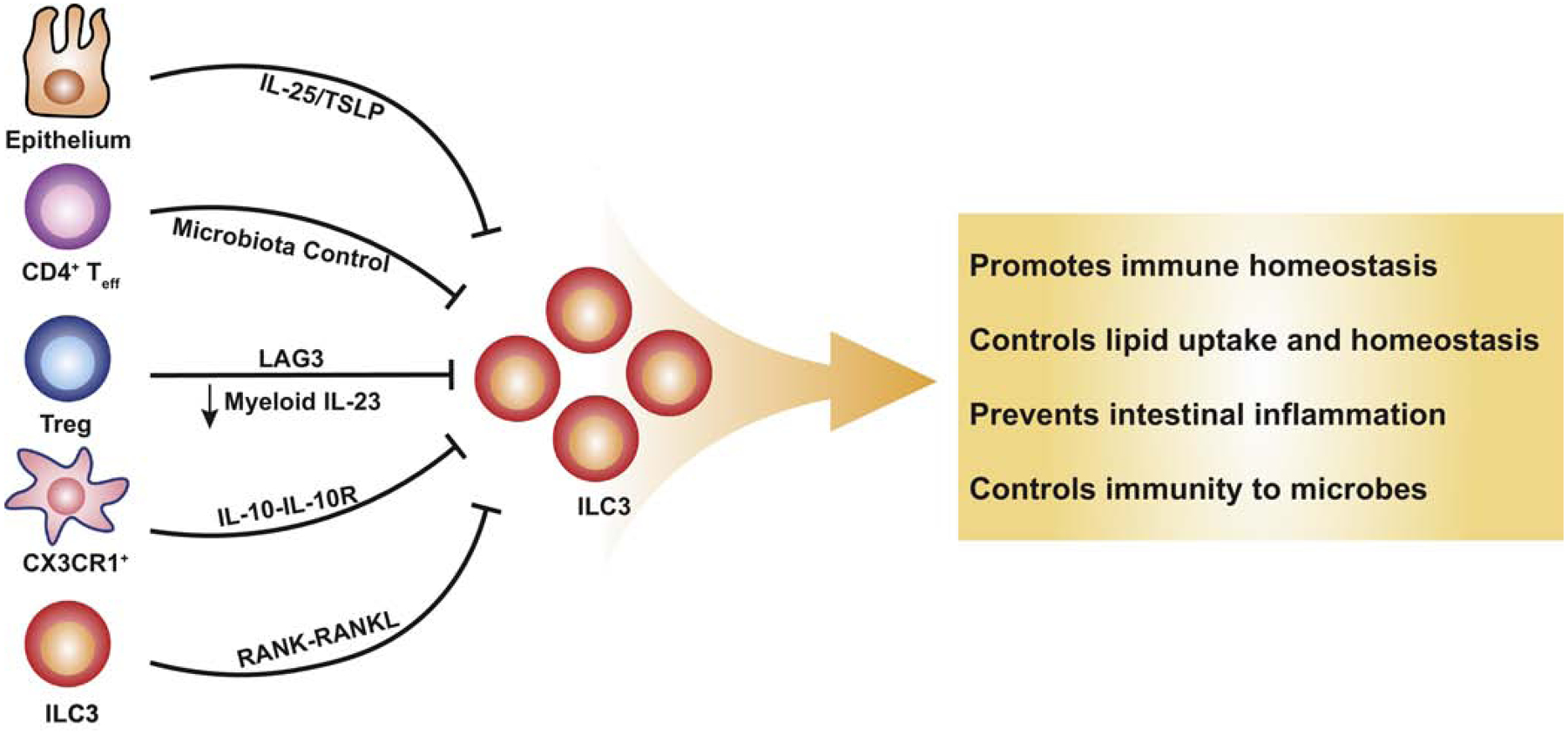
Signals derived from the epithelium, as well as a result of adaptive and innate immunity, suppress the function of ILC3s. Intestinal epithelial cells release IL-25 and TSLP indirectly inhibiting the production of IL-22 in ILC3s. Both CD4+ effector T cells and regulatory T cells are able to indirectly suppress ILC3s through distinct mechanisms. IL-10 signaling in CX3CR1+ myeloid cells indirectly repress ILC3s and RANK signaling enables self-regulation of ILC3s. Downward arrows represent suppression.
