Figure 1.
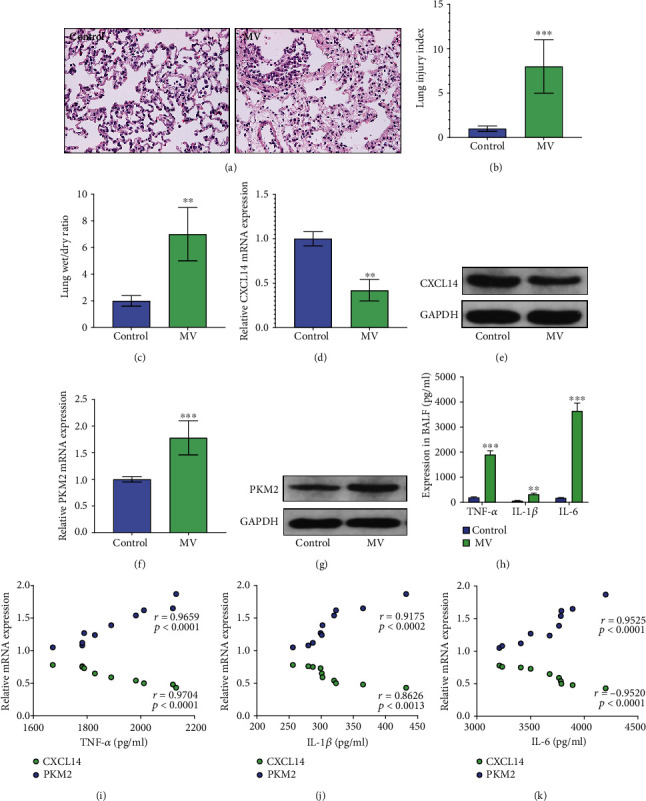
MV induced excessive production of proinflammatory cytokines together with downregulated CXCL14 and upregulated PKM2 expressions in the lungs. H&E stain (a) demonstrated apparent histological damages in the lungs after MV. In addition, lung injury index (b) and wet/dry ratio (c) were significantly increased in the MV group as compared with the control group. RT-PCR (d) and Western blots (e) demonstrated that pulmonary CXCL14 were significantly downregulated by MV, whereas expressions of PKM2 were significantly increased after MV (f, g). ELISA assays (h) showed that proinflammatory cytokines including TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 were significantly increased in the MV group as compared with the control group. Moreover, correlation analysis (i–k) indicated that CXCL14 expressions were negatively, whereas PKM2 were positively associated with proinflammatory cytokines. ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.0001 vs. the control group.
