Figure 2.
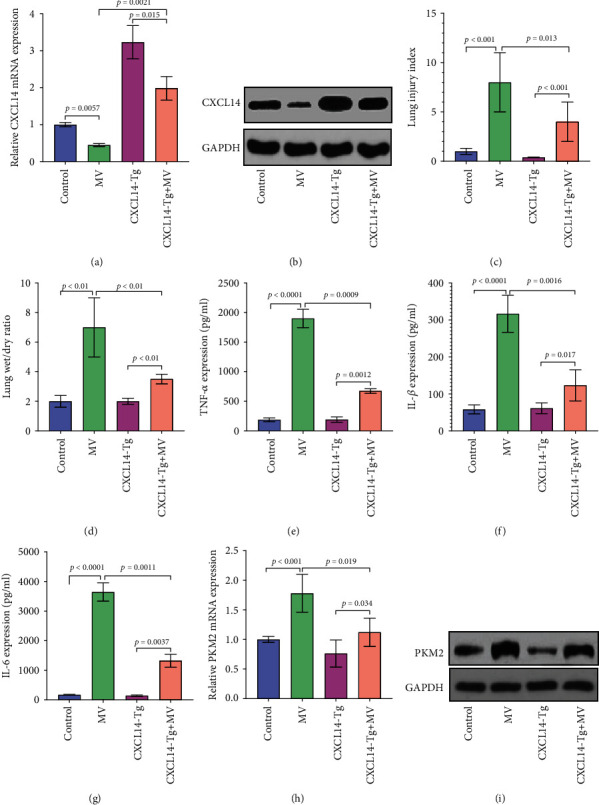
CXCL14 overexpression attenuated VILI and downregulated pulmonary PKM2 and cytokine expressions. RT-PCR (a) and Western blots (b) showed increased pulmonary expressions of CXCL14 in the CXCL14-Tg mice as compared with the wild-type mice (control and MV groups), indicating an overexpression of CXCL14. CXCL14-Tg mice showed improved pulmonary morphology as reflected by decreased lung injury index (c) and wet/dry ratio (d) as compared with wild-type mice (MV group). Moreover, proinflammatory cytokines including TNF-α (e), IL-1β (f), and IL-6 (g) were markedly decreased in the CXCL14-Tg+MV group as compared with the MV group. Moreover, RT-PCR (h) and Western blots (i) showed significantly lower expressions of PKM2 in the CXCL14-Tg mice than in the wild-type mice after MV.
