Figure 2.
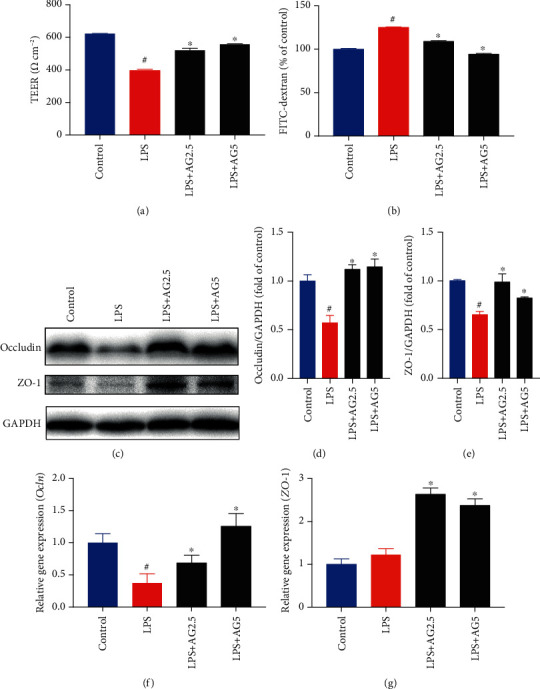
Andrographolide improved LPS-induced disruption of the intestinal barrier in Caco-2 cells. (a) Effect of andrographolide on TEER in LPS-induced Caco-2 cells. The Caco-2 cells were seeded in Transwell cell plates and cultured for 21 days to form a cell monolayer. Then, the cells were treated with andrographolide (2.5 and 5 μM) for 24 h, followed by the treatment of LPS (10 μg/mL) for a further 24 h. The TEER value was measured using a Millicell-ERS-2 Volt-Ohm meter (Millipore). (b) Effect of andrographolide on FITC-dextran concentration. The Caco-2 cells in Transwell cell plates were treated with andrographolide (2.5 and 5 μM) for 24 h, followed by the treatment of LPS (10 μg/mL) for a further 24 h. After treatment, the medium in the apical compartment was replaced with fresh DMEM containing FITC-dextran (1 mg/mL). After 2 h incubation, the medium from the basolateral compartment was subjected to spectrofluorometric measurement. (c–e) Immunoblot analysis of Occludin and ZO-1 protein expression from LPS-induced Caco-2 cells in the presence and absence of andrographolide (2.5 and 5 μM) for 24 h. The protein bands were subjected to densitometric analysis using ImageJ. Relative mRNA expression of (f) Ocln and (g) ZO-1 were determined by RT-PCR. Data represent means ± SEM (n = 3), #p < 0.05 versus the control group, ∗p < 0.05 versus the LPS group.
