Figure 1. Functional Tregs Are Reduced at the Human Maternal-Fetal Interface in a Subset of Idiopathic PTL and birth.
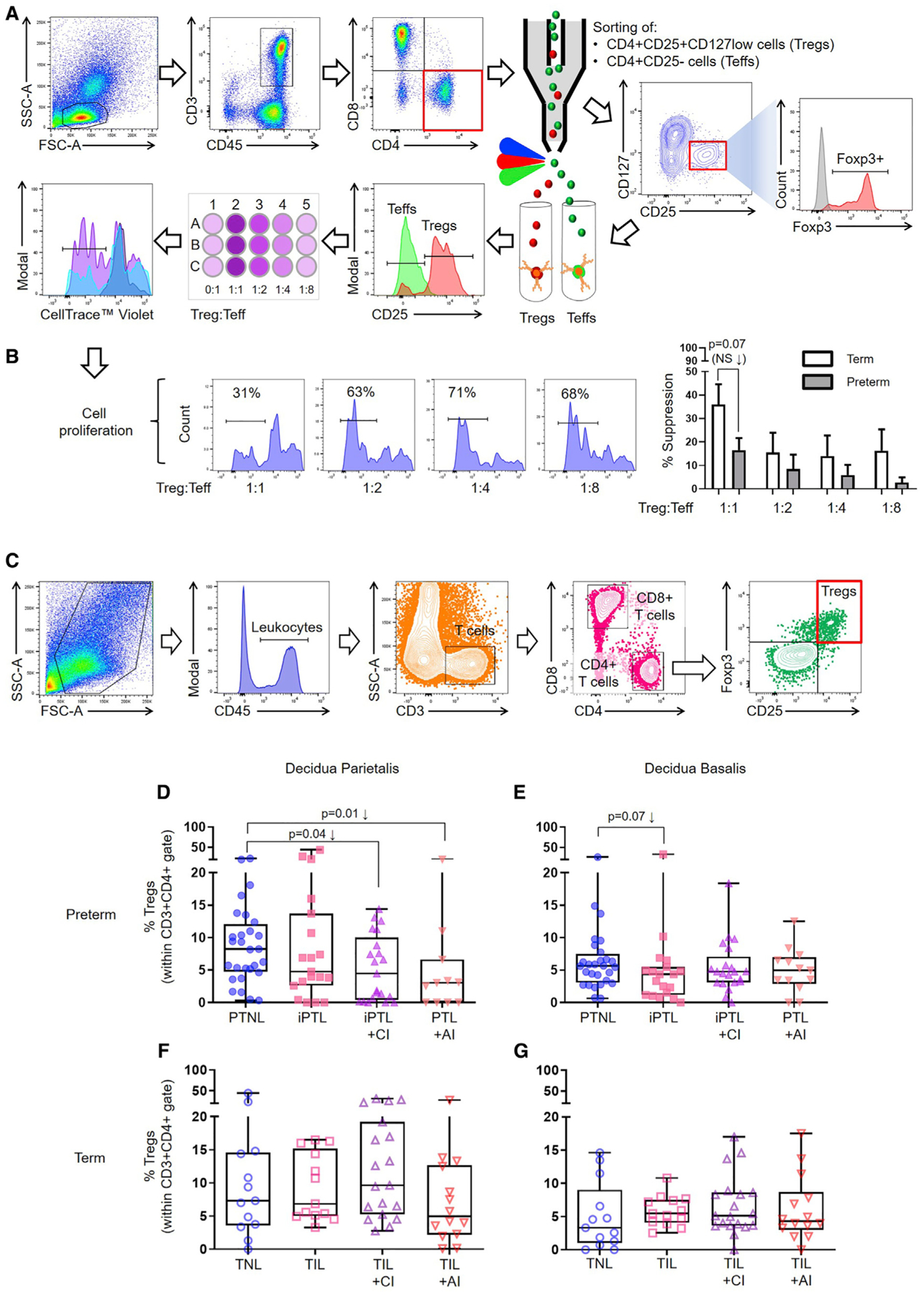
(A) Representative gating strategy used to sort Tregs and Teffs from the decidua. Tregs were co-cultured with Teffs, and Teff proliferation was measured by flow cytometry using CellTrace violet.
(B) Representative plots showing the proliferation of Teffs, with the percentage of decidual Treg suppression of Teffs from preterm and term pregnancies. Suppression data are shown as means ± SEM. n = 6–8 per group.
(C) Representative gating strategy used to identify Tregs in the decidua parietalis and decidua basalis.
(D and E) Frequency of Tregs in the (D) decidua parietalis (n = 11–28 per group) or (E) decidua basalis (n = 13–28 per group) of women with PTNL, iPTL, iPTL+CI, or PTL+AI.
(F and G) Frequency of Tregs in the (F) decidua parietalis (n = 13–19 per group) or (G) decidua basalis (n = 13–19 per group) of women with TNL, TIL, TIL+CI, or TIL+AI.
Data are represented as medians with interquartile and minimum/maximum ranges. Statistical analysis was performed using the Mann-Whitney U-test. Demographic and clinical characteristics of the study population are shown in Tables S1 and S2.
