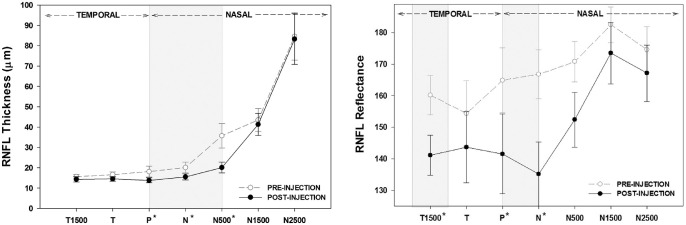
Figure 4.
Change in RNFL thickness and reflectance after anti-VEGF treatment. Anti-VEGF treatment resulted in significant reduction in RNFL reflectance (P < 0.001) and thickness (P < 0.001, Kruskal–Wallis one-way analysis of variance on ranks) at predetermined observation points. Multiple comparison with the Student–Newman–Keuls test revealed significant differences of RNFL reflectance and thickness changes at predetermined loci (P < 0.05) (A) Resolution of the macular edema resulted in significant decrease in the thickness of the RNFL at the peak point of the cyst (P), at its nasal edge (N), and 500 µm nasal to the cyst (N500) (shaded zones). (B) Significant RNFL reflectance changes were observed after the resolution of the macular edema (P < 0.001). RNFL reflectance decreased significantly at the edema's peak (P = 0.037), nasal border (P = 0.02), and 1500 µm (P = 0.022) away from the temporal edge (shaded zones). Bars represent the standard error.