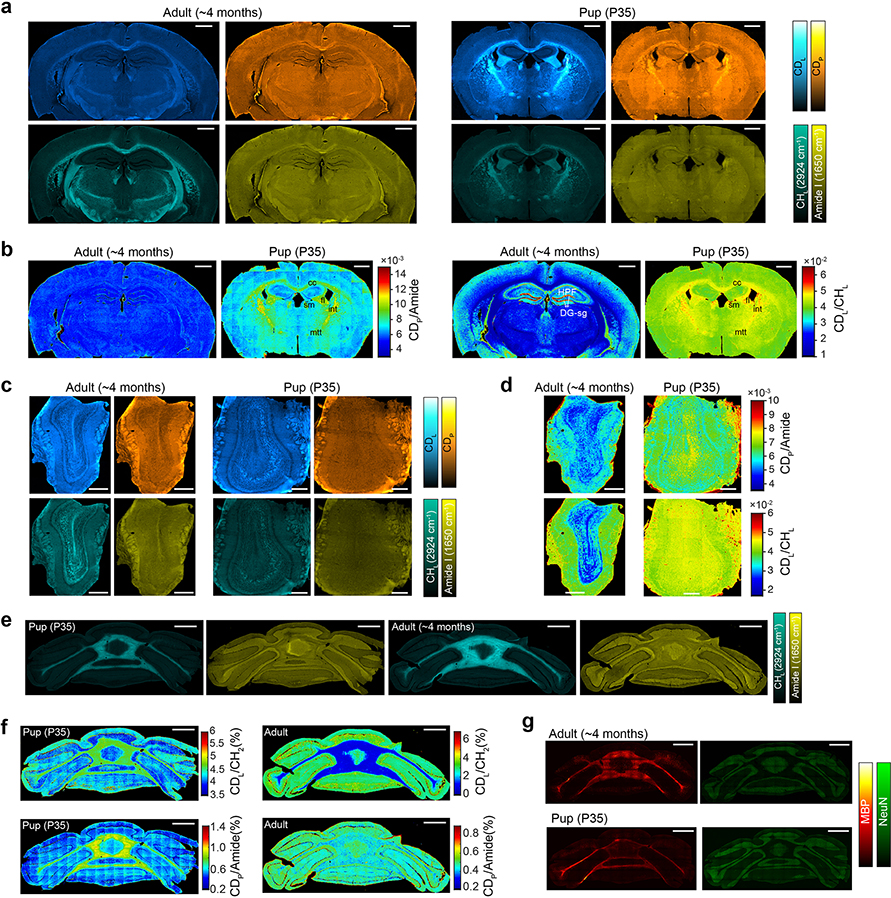
Extended Data Fig. 6 |. MIR imaging of brain metabolic activities during development.
a, b, CDL, CDP, Amide I and CHL FTIR images (a) and generated maps of protein synthesis and de novo lipid synthesis activities (b) on brains of adult and young mouse. cc: corpus callosum; fi: fimbria; sm: stria medullaris; int: internal capsule; mtt: mammilothalmic tract; HPF: hippocampus; DG-sg: granule cell layer of dentate gyrus. c, d, FTIR images (c) and generated maps of protein synthesis and de novo lipid synthesis activities (d) on olfactory bulb of adult and young mouse. P35 is 35 days postnatal mice given with 25% D2O in drinking water for P1-P35 duration and adult mice were also labeled with 25% D2O in drinking water for 35 days. e, f, FTIR images (e) and generated maps of protein synthesis and de novo lipid synthesis activities (f) on cerebellum of adult and young mouse. Experiments in a-f were repeated on three tissue slices each with similar results. (g) Immunofluorescence imaging of myelin basic protein (MBP) and NeuN (neuronal nuclei) on adult and young mouse. NeuN is mainly restricted to granular layer of cerebellum. Experiments were not repeated. Scale bars, 1 mm in a, b and e-g, 500 μm in c, d.