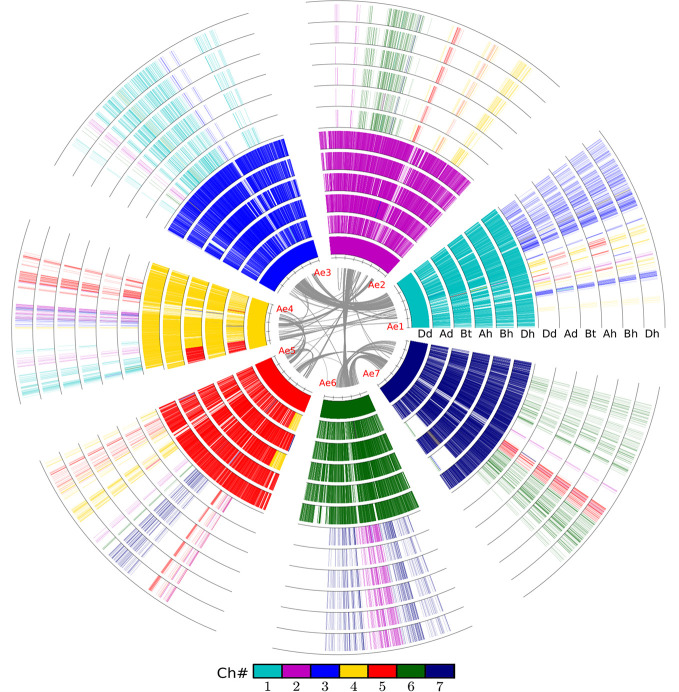
Figure 1.
Alignment of the wheat and relative genomes with wheat DD as reference. The whole-genome duplication (WGD) in the common grass ancestor of plants caused them to have at least two circles of chromosomes. The hybridization event caused common wheat to have six such chromosomes. The innermost circle represents the seven chromosomes of the wheat DD genome (Dd) from Aegilops tauschii, and the gray lines linking paralogous genes. Ad, Triticum urartu; Bt, subgenome B in tetraploid wild wheat; Ah, Bh, and Dh, three subgenomes of common wheat.