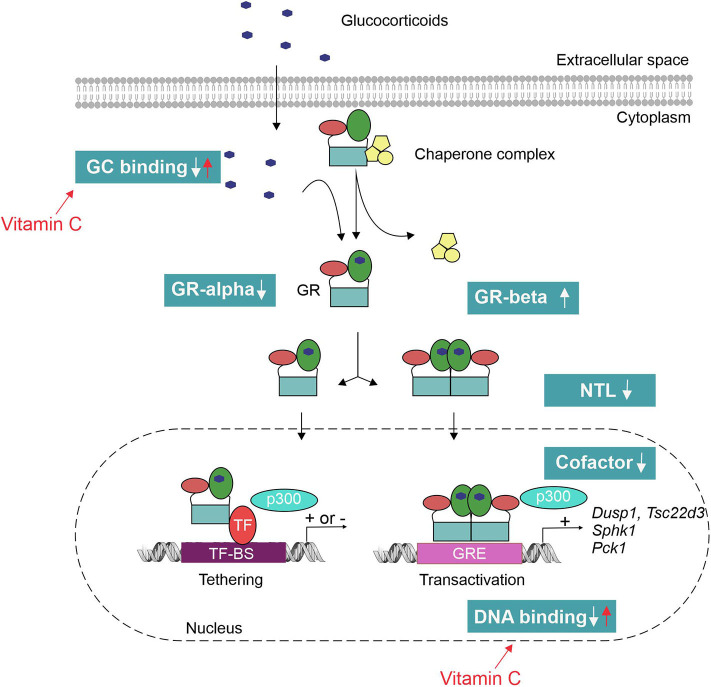
Figure 3.
Mechanisms of glucocorticoid resistance (GCR) in sepsis. Pro-inflammatory cytokines and oxidative stress have shown to interfere with the GC signaling pathway at multiple levels. This leads to an inadequate response of the GR to both endogenous (cortisol/corticosterone) and exogenous GCs to tolerate collateral damage induced by sepsis. Vitamin C has been shown to restore the GR function by reverting the effect of oxidative stress on GR's ligand- and DNA-binding capacity. TF-BS, transcription factor binding site; GRE, GC-responsive element; NTL, nuclear translocation.