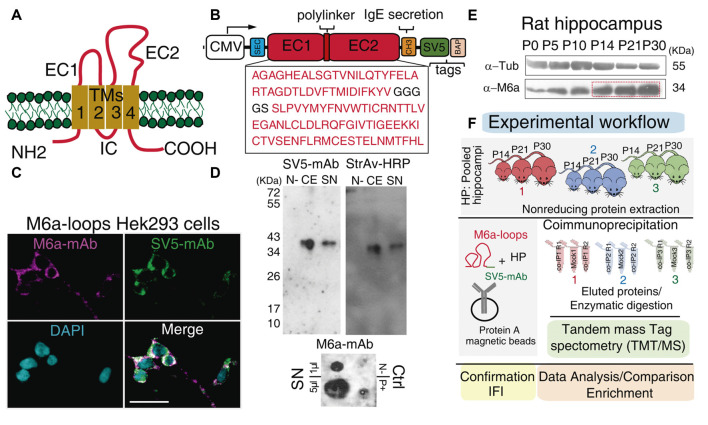
Figure 1.
Workflow: from the chimera protein to co-immunoprecipitation and protein identification. (A) Schematic representation of M6a: it has four transmembrane domains (TM1-4), two extracellular loops, a small (EC1) and a large (EC2), an intracellular loop (IC) and the N- and C-terminus at the cell cytoplasm. (B) Scheme of the chimera protein: M6a-loops construct. The EC1 and EC2 of rat M6a (NCBI Reference Sequence: NP_835206.1), were cloned into the pBig plasmid. White box: CMV promoter, blue box: secretion signal peptide, SEC, red boxes: EC1, EC2, and the polylinker peptide, orange box: IgE secretion sequence, green box: SV5 tag and pink box: biotin acceptor peptide (BAP) tag. (C) M6a-loops-HEK293 cells were labeled with structural anti-M6a-mAb (magenta), anti-SV5-mAb (green), and the superposition of both channels is shown in white (Merge). Cells nuclei were stained with DAPI. Scale bar: 30 μm. (D) Representative Western blots (top panels) and Dot blot (DB, bottom panel) of cell extracts (CEs) and concentrated supernatants (SN) from M6a-loops-HEK293 cells and culture media respectively. Non-transfected HEK293 cells were used as the negative control. Rat hippocampi homogenates were used as a positive control in DB. Anti-SV5-mAb and Streptavidin-HRP were used to characterize the expression and secretion of M6a-loops. DB was done under non-denaturing conditions and 1 μl and 5 μl of M6a-loops from SN (0.5 mg/ml) were used. (E) Representative Western blot of rat hippocampus from postnatal day 0 (P0) to P30. Primary antibodies used were anti-M6a:COOH and anti-tubulin as the loading control. (F) Workflow of the co-IP-TMT/MS experiment. M6a-loops was captured with anti-SV5-mAb cross-linked into protein A magnetic beads. After, protein extracts from rat hippocampi homogenates of postnatal days 14, 21, and 30 (n = 3 animals per co-IP, one animal of each P day per experiment) were co-immunoprecipitated with M6a-loops. A total of three co-IPs were performed with their replicates (n = 9). Eluted proteins were enzymatically digested and peptides were subjected to TMT/MS. Finally, we performed data analysis, gene ontology (GO) enrichment analysis, and validation of these results.