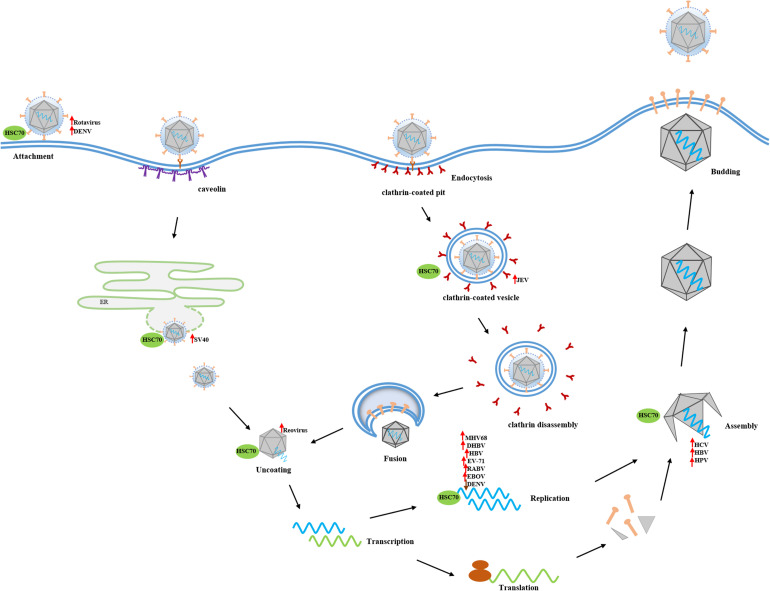
FIGURE 2.
The broad spectrum of HSC70 functions in virus infections. As a multitask chaperon protein, HSC70 is hijacked to be involved in many decisive aspects of virus infection. Membrane-anchored HSC70 acts as binding receptor or post-attachment receptor to facilitate the entry of DENV and rotavirus into host cells, respectively. After crossing the membrane barrier, HSC70 contributes to viral disassembly through uncoating clathrin from CCV or assisting in releasing capsid protein in an ATP-dependent manner. Subsequently, HSC70 positively or negatively participates in the replication stage of some viruses, such as MHV68, DHBV, HBV, EV-71, RABV, EBOV, and DENV, through interacting with viral proteins or viral genome. Finally, HSC70 promotes viral morphogenesis generally via interacting with capsid protein. The up arrow means HSC70 positively regulates the viral infection stage, and conversely, down arrow means HSC70 exerts a negative effect on the viral infection stage.