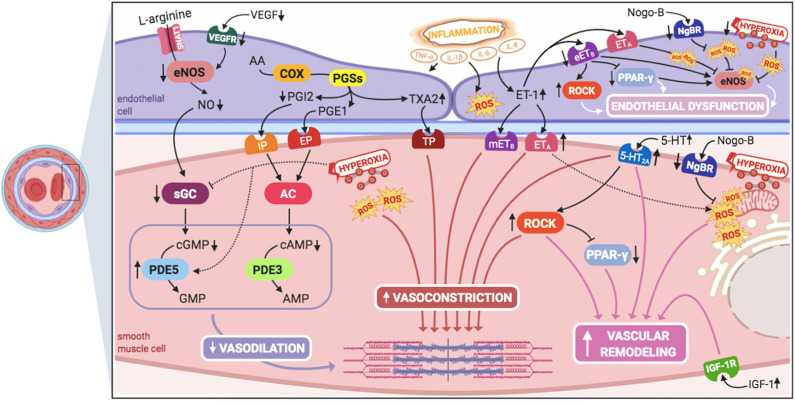
Figure 1.
Signaling pathways involved in the pathogenesis of persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn (PPHN) and its interactions. 5-HT, serotonin; 5-HT2A, 5-HT receptor 2A; AA, arachidonic acid; AC, adenylyl cyclase; AMP, adenosine monophosphate; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; cGMP, cyclic guanylyl monophosphate; COX, cyclooxygenase; eETB, endothelial relaxant endothelin receptor B; eNOS, nitric oxide synthase; EP, PGE1-receptor; ET-1, endothelin-1; ETA, endothelin receptor A; GMP, guanylyl monophosphate; IGF-1, insulin growth factor 1; IGF-1R, IGF-1 receptor; IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, interleukins-1β, 6, and 8; IP, PGI2-receptor; mETB, smooth muscle contractile endothelin receptor B; NgBR, Nogo-B receptor; NO, nitric oxide; PDE3, phosphodiesterase-3; PDE5, phosphodiesterase-5; PGE1, prostaglandin E1; PGI2, prostacyclin; PGSs, prostaglandin synthases; PPAR- γ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ; ROCK, Rho-kinase; ROS, reactive oxygen species; sGC, soluble guanylyl cyclase; SNAT1, sodium-coupled neutral amino acid transporter; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor α; TP, TXA2-receptor; TXA2, thromboxane A2; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; VEGFR, VEGF receptor. This figure was created with BioRender.com.