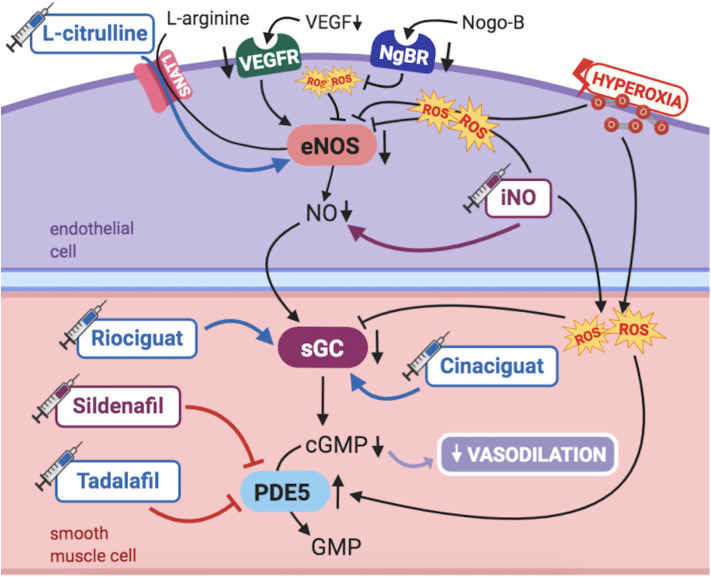
Figure 2.
Pathogenic mechanisms of persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn (PPHN) and its current and potential target therapies: NO-cGMP pathway. cGMP, cyclic guanylyl monophosphate; eNOS, nitric oxide synthase; GMP, guanylyl monophosphate; iNO, inhaled nitric oxide; NgBR, Nogo-B receptor; NO, nitric oxide; PDE5, phosphodiesterase-5; ROS, reactive oxygen species; sGC, soluble guanylyl cyclase; SNAT1, sodium-coupled neutral amino acid transporter; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; VEGFR, VEGF receptor. Target therapies are marked with a syringe icon and are colored based on the type of evidence supporting its use on PPHN—purple, evidence on its was obtained by adequately powered RCTs/meta-analysis; pink, evidence limited to observational studies or small and underpowered RCTs and/or inconsistent results in human newborns; blue, beneficial effects only demonstrated in experimental models of PPHN. This figure was created with BioRender.com.