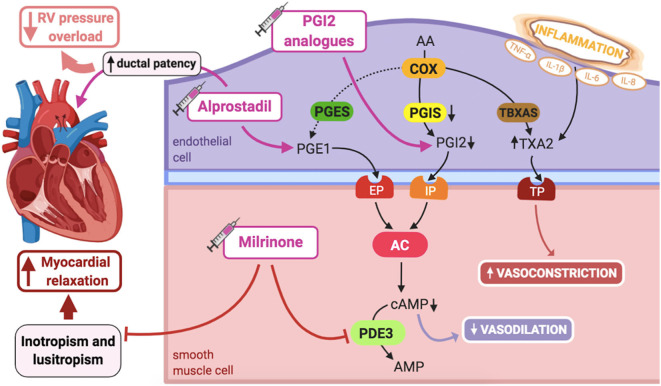
Figure 3.
Pathogenic mechanisms of persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn (PPHN) and its current and potential target therapies: Arachidonic acid-prostacyclin-cAMP pathway. AA, arachidonic acid; AC, adenylyl cyclase; AMP, adenosine monophosphate; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; COX, cyclooxygenase; EP, PGE1-receptor; IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, interleukins-1β, 6 and 8; IP, PGI2-receptor; PDE3, phosphodiesterase-3; PGE1, prostaglandin E1; PGES, PGE1 synthase; PGI2, prostacyclin; PGIS, PGI2 synthase; RV, right ventricle; TBXAS, TXA2 synthase; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor α; TP, TXA2-receptor; TXA2, thromboxane A2. Target therapies are marked with a syringe icon and are colored based on the type of evidence supporting its use on PPHN- Purple: Evidence on its was obtained by adequately powered RCTs/meta-analysis; Pink: Evidence limited to observational studies or small and underpowered RCTs and/or inconsistent results in human newborns; Blue: Beneficial effects only demonstrated in experimental models of PPHN. This figure was created with BioRender.com.