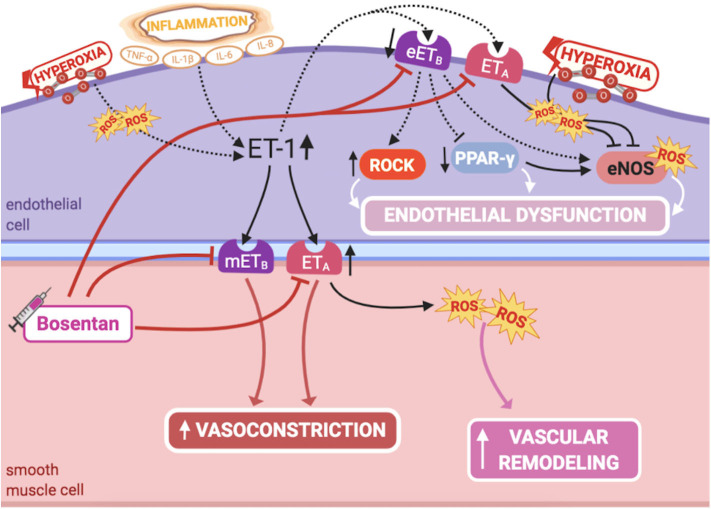
Figure 4.
Pathogenic mechanisms of persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn (PPHN) and its current and potential target therapies: endothelin-1-ETA/ETB receptors. eETB, endothelial relaxant endothelin receptor B; eNOS, nitric oxide synthase; ET-1, endothelin-1; ETA, endothelin receptor A; IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, interleukins-1β, 6 and 8; mETB, smooth muscle contractile endothelin receptor B; PPAR-γ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ; ROCK, Rho-kinase; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor α. Target therapies are marked with a syringe icon and are colored based on the type of evidence supporting its use on PPHN—purple, evidence on its was obtained by adequately powered RCTs/meta-analysis; pink, evidence limited to observational studies or small and underpowered RCTs and/or inconsistent results in human newborns; blue, beneficial effects only demonstrated in experimental models of PPHN. This figure was created with BioRender.com.