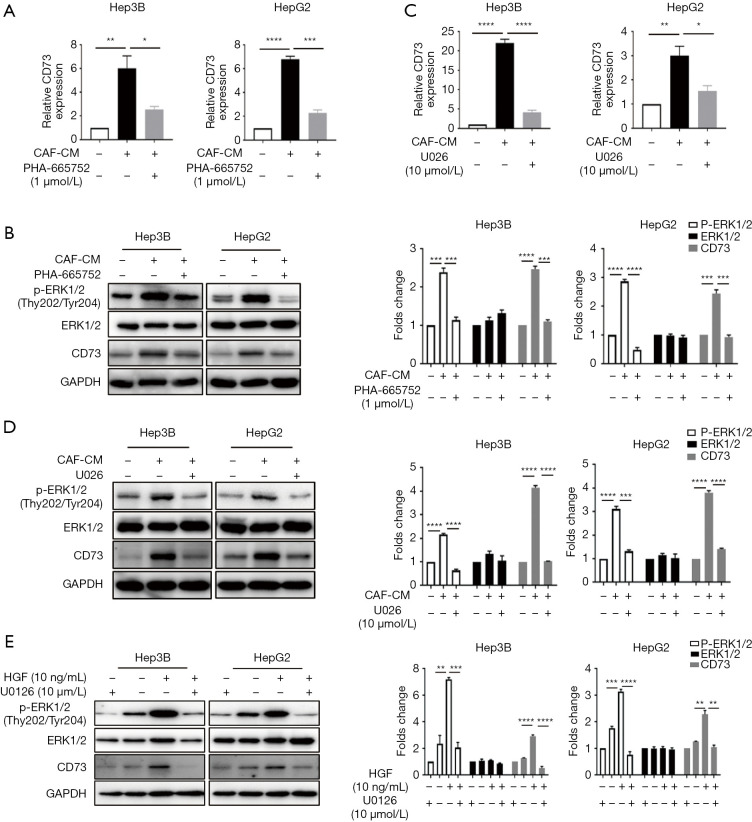
Figure 3.
HGF in CM of CAFs regulated CD73 expression via the MEK-ERK1/2 pathway. (A,B) The effect of CAFs-induced CD73 expression was suppressed after incubation with c-Met inhibitor PHA-665752. CD73 mRNA and protein expression levels were analyzed by qRT-PCR or Western blot. The phosphorylation of ERK1/2 was also inhibited when treated with a c-Met inhibitor; (C,D) Hep3B and HepG2 cells were pre-treated with MEK inhibitor U0126, followed by the incubation of CM of CAFs. Inhibition of MEK abolished CAF-CM-induced CD73 expression and the phosphorylation of ERK1/2; (E) Hep3B and HepG2 cells were pre-treated with U0126 to inhibit MEK, followed by the administration of 10 ng/mL of HGF. The administration of HGF alone promoted CD73 expression in HCC cells. Inhibition of MEK abolished HGF-induced CD73 expression. Data are presented as the means ± SEM of three independent experiments, the quantitative analysis are done for western blot. *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001; ****, P<0.0001, t-test. HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; CM, conditioned medium; CAF, cancer-associated fibroblast; qRT-PCR, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma.