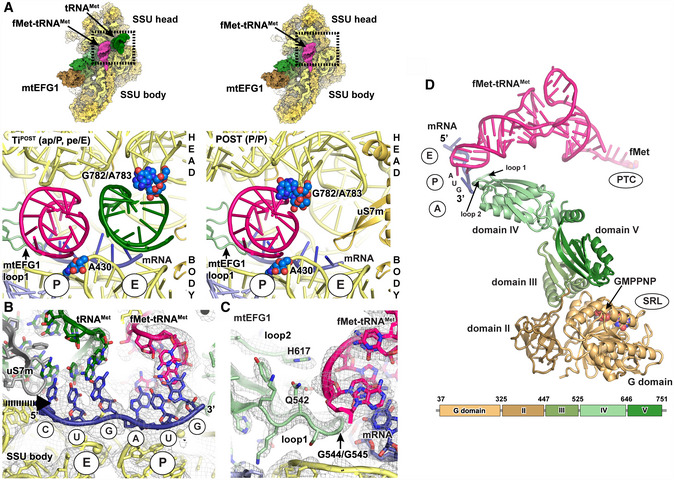
Interactions of the tRNAs in TiPOST and POST states with ribosomal P site elements (blue) of the SSU head (G782/A783 ridge) and body (A430) rRNA. tRNA binding sites of the SSU body are indicated in circles. View from the subunit interface onto the SSU with the enlarged area being highlighted with a box. Left: In the transit TiPOST state, the SSU head is rotated with the G782/A783 ridge moving in concert with deacylated tRNAMet (green). This leads to a repositioning of aminoacylated fMet‐tRNAMet and deacylated tRNAMet into a chimeric ap or pe positions, respectively. Right: In the POST state, the aminoacylated fMet‐tRNAMet (pink) in the P site engages with both head and body elements.
Both tRNAs remain associated with their respective mRNA codons in the TiPOST state. A superposition of the position of the uS7m beta‐hairpin in the unrotated SSU head conformation is displayed in gray to indicate its clash with the deacylated tRNAMet (green) upon backswiveling of the SSU head. The arrow indicates the direction of motion of uS7m. The EM density of the TiPOST state is contoured at 4σ.
Loops 1 and 2 of mtEFG1 domain IV contact the fMet‐tRNAMet‐mRNA module via conserved residues including a di‐glycine motif (G544/G545), Q542 and H617 to prevent slippage of the tRNA and to maintain the mRNA reading frame. The EM density and the structural model are shown for the POST state but are very similar in the TiPOST state (The map is depicted at 4σ).
mtEFG1, fMet‐tRNAMet, and mRNA of the POST state are shown in isolation. The domain organization of mtEFG1 is indicated by different colors. A corresponding schematic representation including the amino acid numbering of domain borders is given at the bottom. Locations of the surrounding ribosomal elements are indicated.