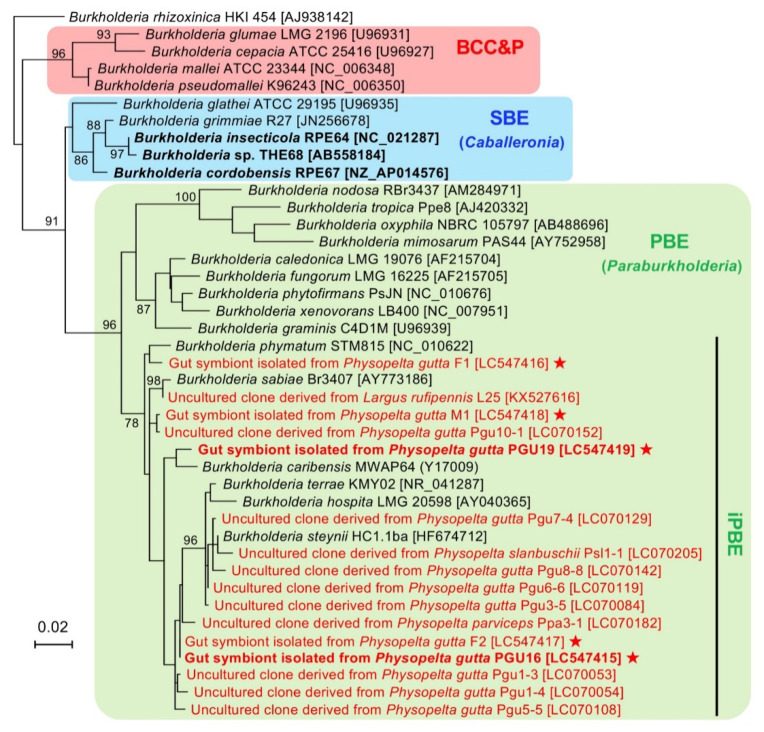
Figure 2.
Molecular phylogeny of the Burkholderia symbionts isolated from P. gutta based on 16S rRNA gene. The tree shows an ML phylogeny of the five isolates and related species/clones of the genus Burkholderia sensu lato. The multiple sequence alignment of 1320 nucleotide sites of the bacterial 16S rRNA gene was analyzed. Accession numbers in the DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank DNA database are shown in square brackets. The isolates and uncultured clones of symbiotic Burkholderia derived from largid stink bugs are shown in red. Stars indicate the isolates reported in this study. Bold indicates the Burkholderia symbionts of stink bugs with complete genome sequences. Bootstrap support values higher than 70% are shown on the internal branches. BCC&P, Burkholderia cepacia complex and Burkholderia pseudomallei clade; SBE, stink bug-associated beneficial and environmental clade; PBE, plant-associated beneficial and environmental clade; iPBE, insect-associated PBE clade.