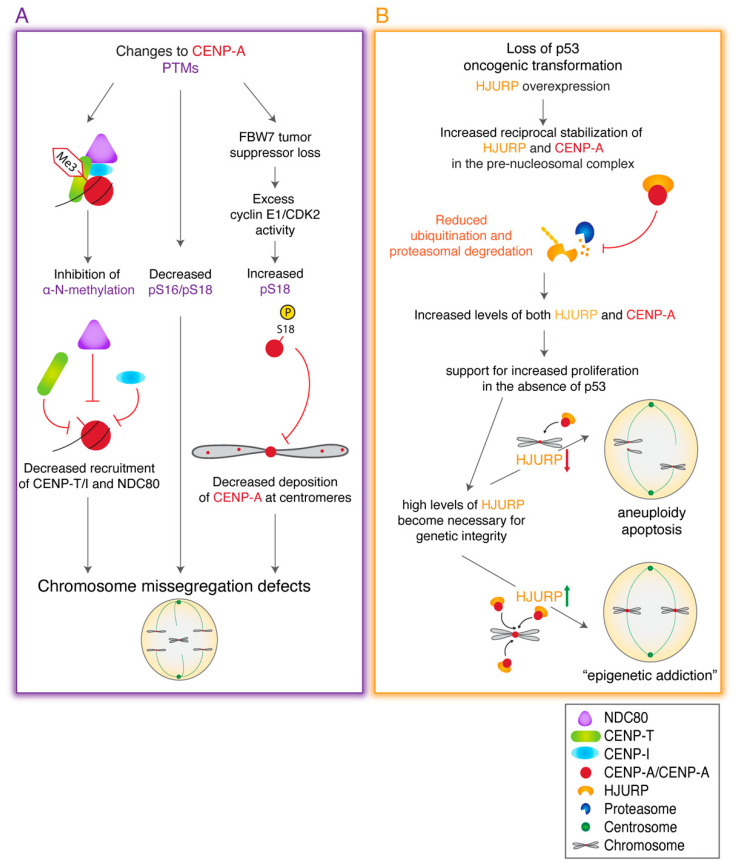
Figure 5.
Alterations to CENP-A PTMs and/or to HJURP expression levels contribute to CIN and tumor progression. (A) Alterations to CENP-A posttranslational modifications (PTMs) can reduce recruitment of CCAN and kinetochore components, reduce CENP-A deposition at centromeres, and lead to chromosome segregation defects. (B) HJURP overexpression stabilizes CENP-A in the pre-nucleosomal complex and CENP-A protects HJURP from degradation. In p53 null cancers, upregulated HJURP levels become critical for maintaining centromere integrity and preventing apoptosis as p53-mediated DNA checkpoints are lost, leading to HJURP epigenetic addiction that contributes to tumor survival and progression.