Fig. 3.
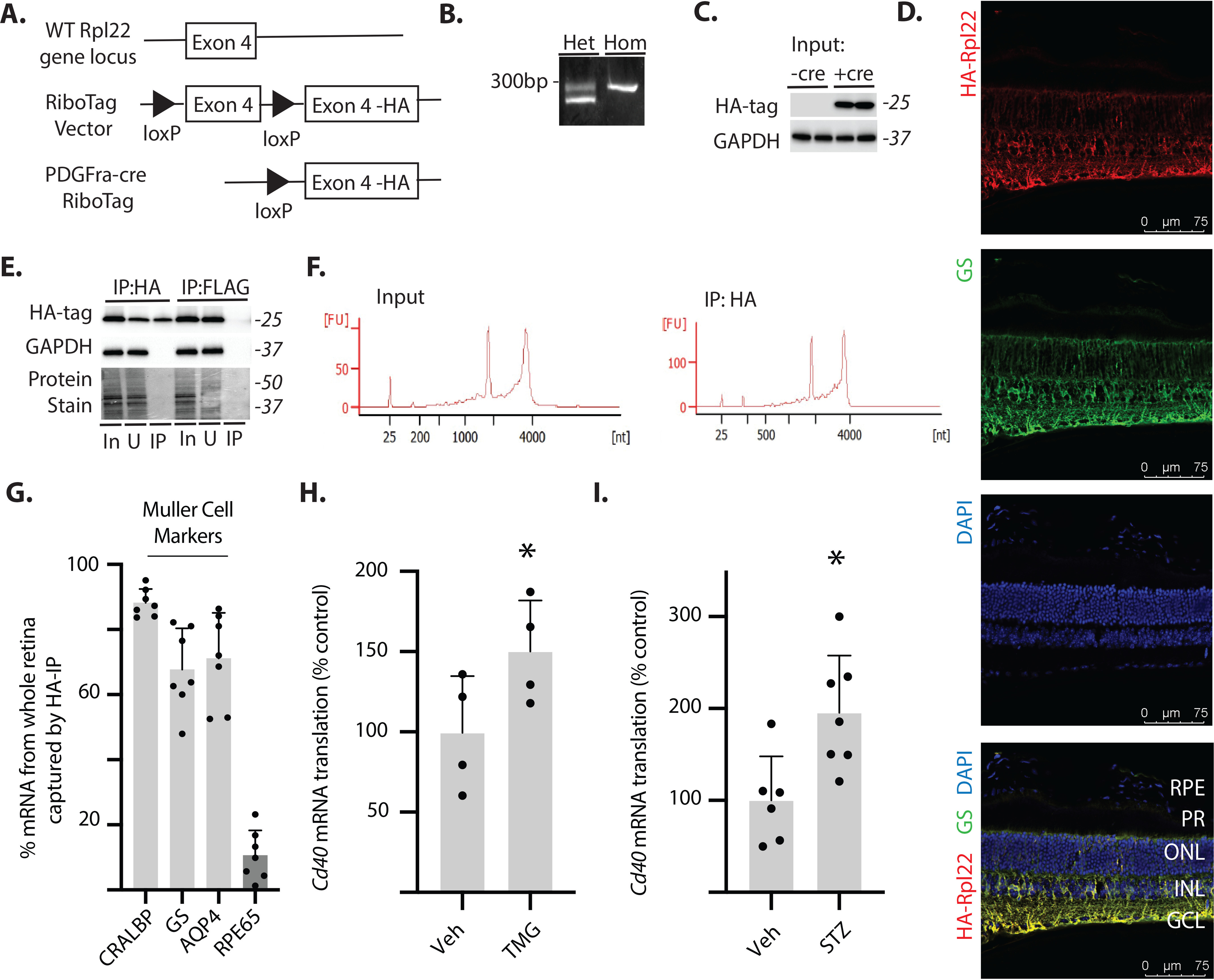
Cd40 mRNA translation is enhanced in retinal Müller glia by O-GlcNAcase inhibition or diabetes. A, Müller glia–specific expression of HA-tagged Rpl22 protein in retina was achieved by crossing WT RiboTag mice to a PDGFRa-cre recombinase–expressing mouse, resulting in deletion of the WT exon 4 in the target cell population and replacement with the Rpl22HA exon. B, PCR products were generated using oligonucleotides that amplify the loxP-containing intron sequence 5′ to the WT exon 4 of the Rpl22 gene. The WT PCR product is 260 bp, whereas the mutant PCR product is 290 bp. C, Western blotting analysis of HA-tagged Rpl22 and GAPDH in retinal lysates from WT Rpl22 (-cre) or Rpl22HA (+cre) mice. D, whole eyes were isolated, fixed, and cryosectioned into sagitally oriented longitudinal cross-sections. HA-Rpl22 (red) and the Müller glia–specific marker GS (green) was evaluated in retinal sections by immunofluorescence. The nuclei were visualized by 4′,6′-diamino-2-phenylindole (DAPI, blue). Colocalization of HA-Rpl22 and GS is shown in yellow. E, ribosomes from Rpl22HA-expressing homozygous mouse retina were isolated by immunoprecipitation. F, bioanalyzer analysis demonstrating recovery of high-quality RNA from both whole retina and following ribosome isolation (RNA Integrity Number >8.0). G, RNA from HA-tag immunoprecipitates was analyzed for recovery of Müller glia–specific markers (CRALBP, GS, and AQP4) and the retinal pigmented epithelia marker RPE65. H and I, Cd40 mRNA association with ribosomes isolated from the retina of Rpl22HA-expressing homozygous mice was determined by PCR. The retinas were isolated from male and female mice 24 h after administration of TMG (H) or from male mice 4 weeks after STZ (I). Protein molecular mass (in kDa) is indicated at right of blots in C and E. The values are means ± S.D. *, p < 0.05 versus vehicle. Het, heterozygous; Hom, homozygous; RPE, retinal pigmented epithelium; PR, photoreceptor outer segments; ONL, outer nuclear layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; IP, immunoprecipitation; GCL, ganglion cell layer; In, immunoprecipitation input; U, unbound immunoprecipitation fraction; Veh, vehicle.
