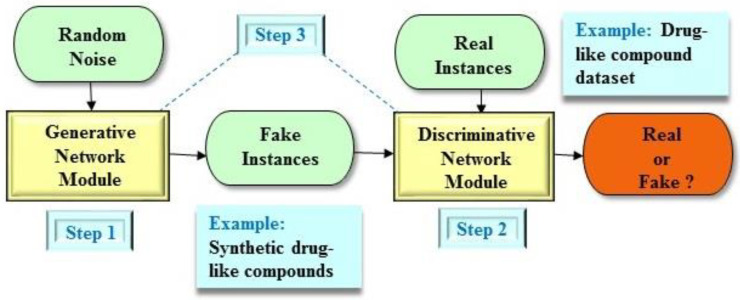
Figure 1.
An example of the generative adversarial network (GAN) architecture. The GAN architecture comprises two main components including a generative network module and a discriminative network module. Step 1: The generative network module produces synthetic instances as real as possible. Gaussian random noises normally serve as the input for the generative network module. One particular example in drug design and discovery is a reconstructed drug-like compound as a fake instance. Step 2: The discriminative network module assesses the probability that an instance stems from the real dataset. One particular example in drug design and discovery is a drug-like compound dataset. Step 3: Both the generative and discriminative network modules play concurrently against each other to obtain their objectives.