Figure 1.
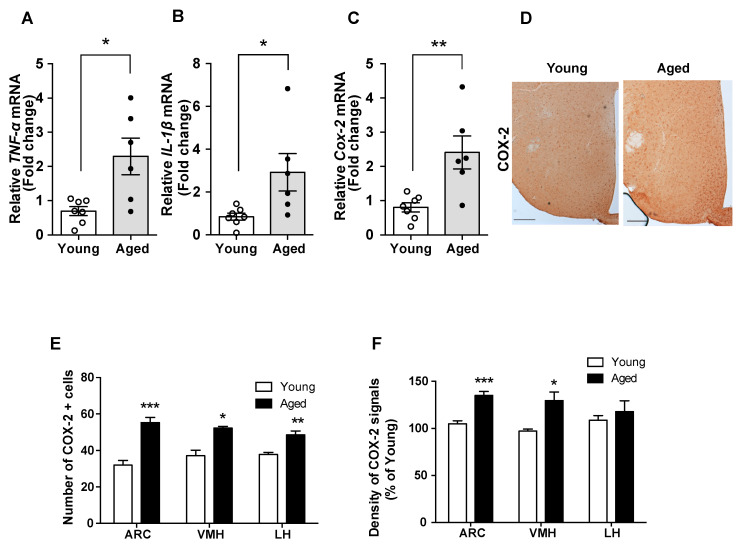
Enhanced hypothalamic inflammation occurred in the aged mice. The comparison between young and aged C57BL/6 mice revealed that the mRNA levels of genes involved in inflammation, such as (A) TNF-α, (B) IL-1β, and (C) COX-2, are increased in hypothalamic samples from aged mice. (D) Representative images showing the immunosignals of COX-2 in the hypothalamus of young and aged mice. Quantification of (E) the number of COX-2-positive cells and (F) the intensity of COX-2 immunoreactive signals in hypothalamic nuclei such as the arcuate nucleus (ARC), ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus (VMH), and lateral hypothalamus (LH) reveals that these parameters are higher in aged mice compared with young mice. The results are presented as the means ± SEMs. n = 6–7 for each group. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 for the aged group versus the young group. Scale bar = 100 μm.