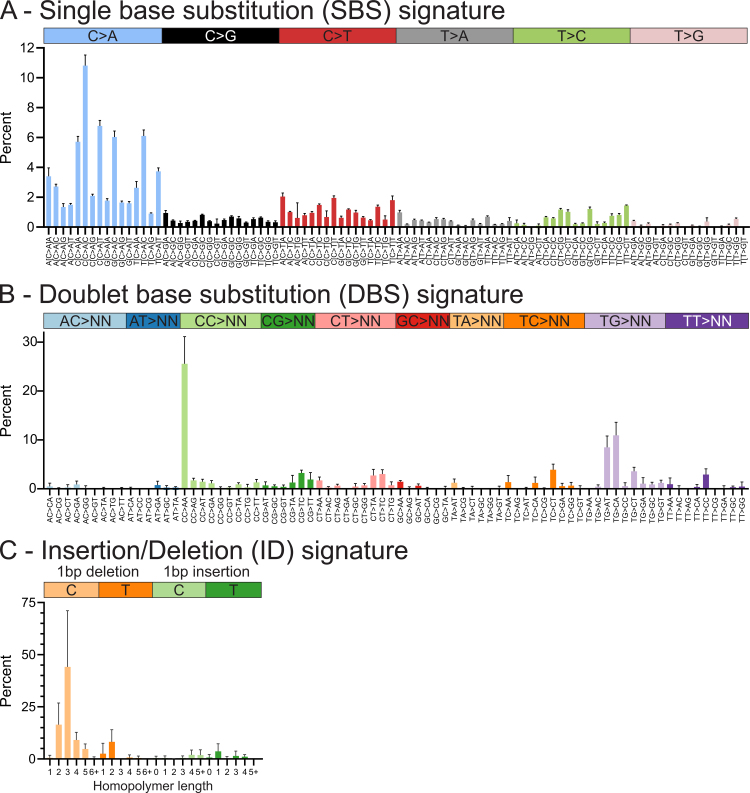
Fig. 2.
Mutational signatures derived from BaP-exposed functionally differentiated NHU cells. (A) Single-base substitution (SBS) signature of 96 subtypes based around six substitution classes (referred to by the pyrimidine of the mutated Watson-Crick base pair) and framed by their 3′ and 5′ flanking nucleotides. The SBS signature shows an enrichment of diverse C > A transversions. (B) Doublet-base substitution (DBS) signature of 78 strand-agnostic mutation types show an enrichment mainly of CC > AA. TG > AT and TG > CA substitutions were additionally observed and were previously reported following BPDE exposure of iPS cells [5]. (C) Insertions/deletion (ID) signature reveals BaP-caused single C/G deletions most commonly in homopolymer runs of two to four cytosines/guanines (n = 4 independent BaP-exposed clones normalised to n = 3 independent control clones; bars indicate the mean and error bars denote the standard deviation). Data in this figure are expressed as percentages; for counts and normalisation data, see Supplementary Figures 2–4. BaP = benzo[a]pyrene; BPDE = benzo(a)pyrene diol epoxide; iPS = induced pluripotent stem; NHU = normal human urothelial.