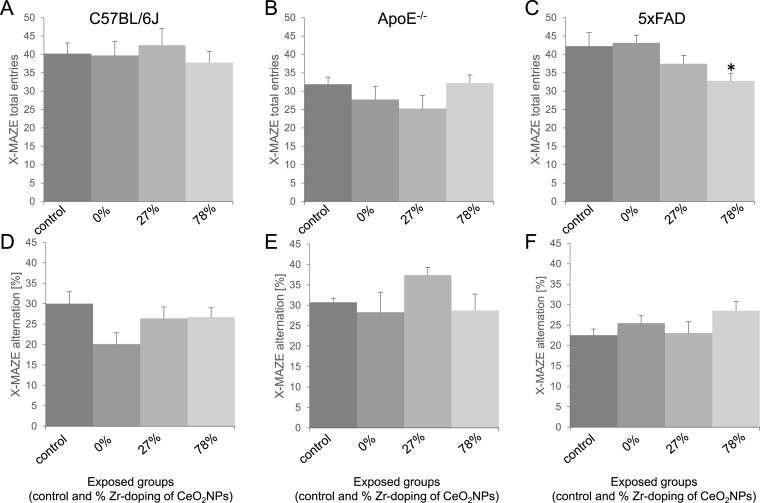
Fig. 2.
Effects of redox-modified CeO2 on performance in the X-maze task.
Female C57BL/6J (A, D), ApoE-/- (B, E) and 5xFAD (C, F) mice were exposed to clean air (control) or CeO2 and 27% ZrO2-doped CeO2 or 78% ZrO2-doped CeO2 NPs via inhalation. After this treatment, the differently exposed groups were subjected to the X-maze task. Mice were place in the maze for 5 min. The behavioural parameters analysed were total arm entries (A, B, C) and alternation (D, E, F) and expressed in mean ± SEM. *Statistical significance different from the respective control in Dunnet post-hoc test following one-way ANOVA with p < 0.05. Number of animals per group: ApoE-/-: control (n = 8); CeO2 (n = 7); 27% ZrO2-doped CeO2 (n = 8); 78% ZrO2-doped CeO2 (n = 8). 5xFAD: control (n = 16); CeO2 (n = 15); 27% ZrO2-doped CeO2 (n = 16); 78% ZrO2-doped CeO2 (n = 16). C57BL/6J: control (n = 10); CeO2 (n = 10); 27% ZrO2-doped CeO2 (n = 10); 78% ZrO2-doped CeO2 (n = 10).