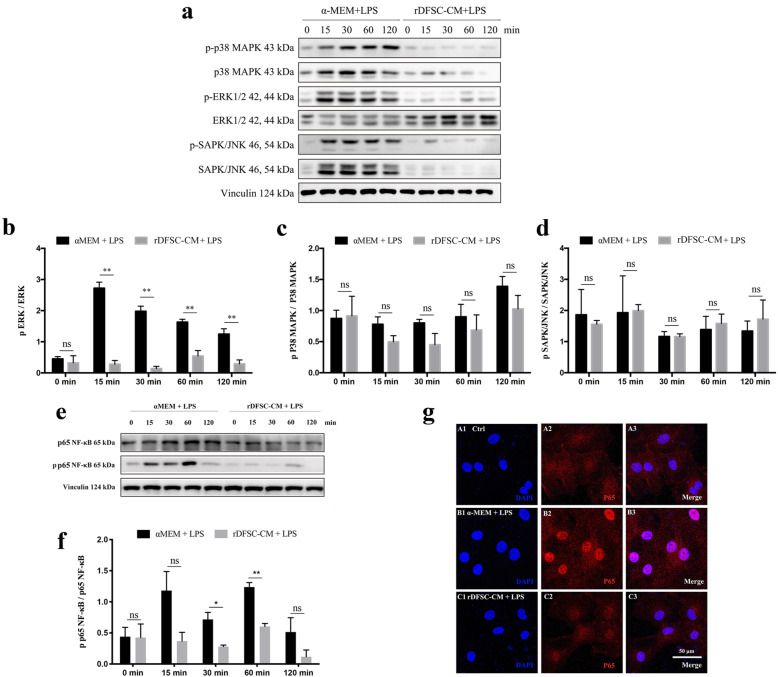
Fig. 3.
Effects of rDFSC-CM on MAPK and NF-κB signaling in inflammatory rDPCs. Cells were cultured until reaching 80% confluence, the medium was then changed to rDFSC-CM or αMEM containing 0.5 mg/L LPS, and the cells were then incubated for 0, 15, 30, 60, and 120 min. The activation of the MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways was detected by a Western blot analysis of total cellular proteins and immunofluorescence staining. a Phosphorylation levels of ERK 1/2, p38 MAPK, and SAPK/JNK. Representative photographs of immunoblots are shown. The molecular weights of the bands are indicated in kilodaltons. b–d Relative densitometry analysis of the aforementioned proteins showed that rDFSC-CM significantly suppressed the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 but not that of p38 or SAPK/JNK. e Phosphorylation level of NF-κB p65. f A relative densitometry analysis of NF-κB p65 showed that p65 phosphorylation increased and peaked at 60 min after LPS treatment but was decreased by rDFSC-CM treatment. g The subcellular localization of NF-κB p65 after treatment with rDFSC-CM for 60 min was determined by immunofluorescence staining with Alexa Fluor 546-conjugated secondary antibody. DAPI was used for DNA staining. Representative images of three independent experiments are shown (scale bar 50 μm). The data are presented as the means ± SDs from at least three independent experiments. **P < 0.01; ns, no significant difference