Figure 1.
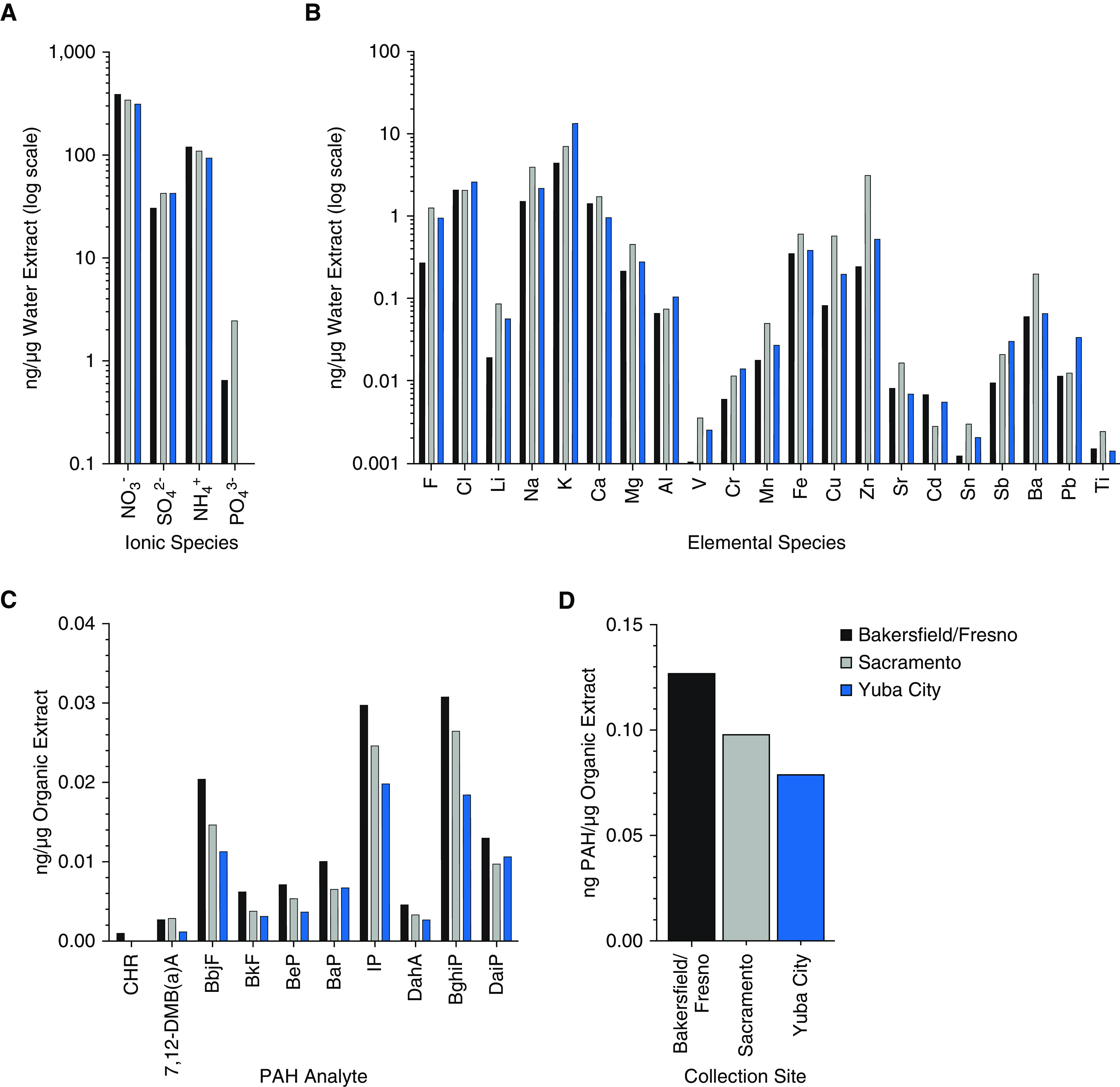
Chemical analysis of urban air pollution particulate matter <2.5 μm (PM2.5) extracts. (A) Relative abundance of ionic chemical species per microgram of water-soluble extract (WE) detected by ion chromatography. (B) Relative abundance of inorganic elemental chemical species per microgram of WE detected by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. (C) Relative abundance of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) species per microgram of organic extract (OE) detected by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. (D) Combined concentration of all assayed PAH species for each pool. BaP = benzo[a]pyrene; BbjF = benzo[bj]fluoranthene; BeP = benzo[e]pyrene; BghiP = benzo[g,h,i]perylene; BkF = benzo[k]fluoranthene; CHR = chrysene; DahA = dibenz[a,j]anthracene; DaiP = dibenz[ai]pyrene; IP = indeno[1,2,3-c,d]pyrene.
