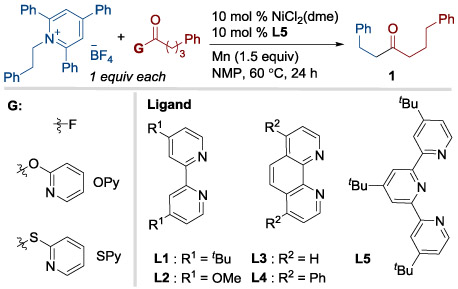
Table 1.
Optimal conditions for primary pyridinium salts.
 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Entry[a] | Change in condition from scheme | G | 1 (%)[b] |
| 1 | None | F | 82 (79) |
| 2[c] | In situ formation of acyl fluoride | F | 75 |
| 3 | L1 instead of L5 | F | 62 |
| 4 | L2 instead of L5 | F | 65 |
| 5 | L3 instead of L5 | F | 53 |
| 6 | L4 instead of L5 | F | 41 |
| 7 | Different G | SPy | 4 |
| 8 | Different G | OPy | 11 |
| 9[e] | Zn instead of Mn | F | 5 |
| 10[d] | No nickel | F | 0 |
| 11[d] | No ligand | F | 0 |
| 12[e] | No Mn reductant | F | 0 |
Pyridinium salt (0.125 mmol, 1 equiv), acyl fluoride (0.125 mmol, 1 equiv), NiCl2(dme) (0.0125 mmol, 10 mol %), ligand (0.0125 mmol, 10 mol %), Mn (0.1875 mmol, 1.5 equiv) was stirred in NMP (0.8 mL) at 60 °C for 24 h.
GC yield vs 1,3.5-trimethoxybenzene standard. Isolated yield in parentheses.
Carboxylic acid (0.125 mmol, 1 equiv), TFFH (0.125 mmol, 1 equiv), 1,8-bis(dimethylamino)naphthylene (0.125 mmol, 1 equiv), NMP (0.8 mL).
Significant amount of acyl fluoride recovered.
Both starting materials recovered.
G = Activating Group.
