Figure 7.
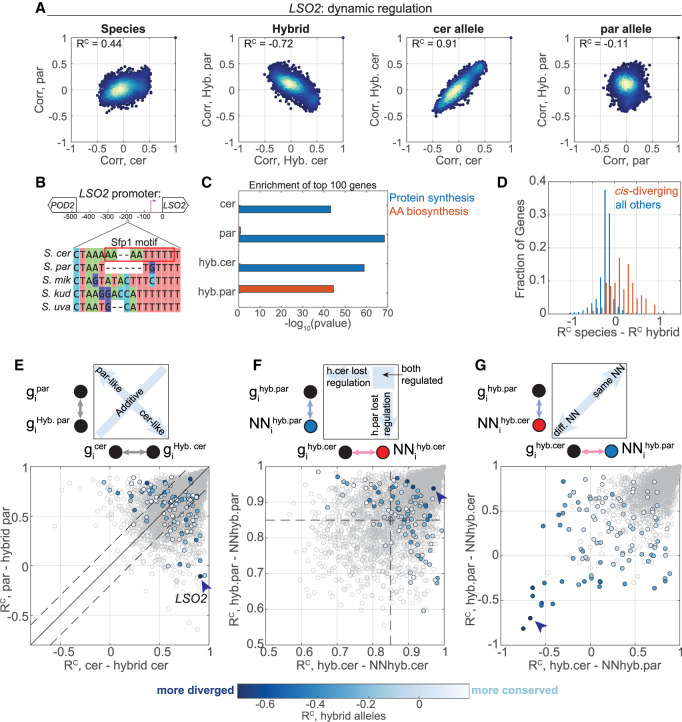
Cis-variations in dynamic regulation are often compensated by trans effects. (A–C) LSO2 is an example for a cis-varying gene. Scatters of coexpression vectors of the indicated comparisons, similar to Figure 5A. (B) S. cerevisiae LSO2 promoter contains a Sfp1 motif. A segment of a sequence comparison of the promoters from the indicated species is shown. (C) Enrichment of ribosomal protein-coding genes, and of amino acid biosynthesis genes, within the top 100 LSO2 correlating genes in the different genetic backgrounds. (D) Cis-variations are compensated by trans-variations. Histogram of the RC difference (between species – between hybrid alleles) for all genes and for cis-varying genes (106 genes). (E) Cis-variations are not typically dominant. The RC scores of cis-diverging genes (color, 106 genes) and of all genes (gray) of the comparison between each species and its corresponding hybrid allele are shown, as in Figure 5E. Color code represents regulatory similarity between hybrid alleles. (F) Half the cis-diverging genes lost regulation in one of the alleles. The RC scores of each gene with its NN in each species are shown, similar to Figure 5F. Color code as in E. (G) Cis-variation involves a change in the nearest neighbor. Cross-species NN similarities are shown, as indicated by the scheme at the top, similar to Figure 5G. Color code as in E.