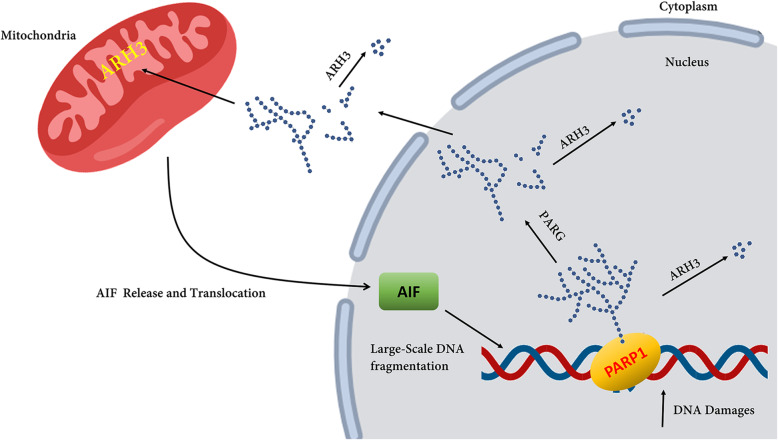
Fig. 3.
Model for the role of ARH3 (encoded by the ADPRHL2 gene) in PAR degradation and apoptosis-inducing factor-mediated cell death. The PARP1 activation triggered by DNA damage leads to poly-ADP ribosylation of PARP1 and other acceptor proteins in the nucleus. Poly (ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase (PARG) hydrolyzes PAR added to the target protein, e.g. PARP1, hence facilitating the protein’s translocation to the cytoplasm and mitochondria. ARH3 hydrolyzes PAR. In the nucleus, AIF recruits various nucleases, e.g. cyclophilin A and H2AX, leading to large-scale DNA fragmentation. There is a general belief that ARH3 is also located in the mitochondrial matrix. The figure is redrawn from [32]