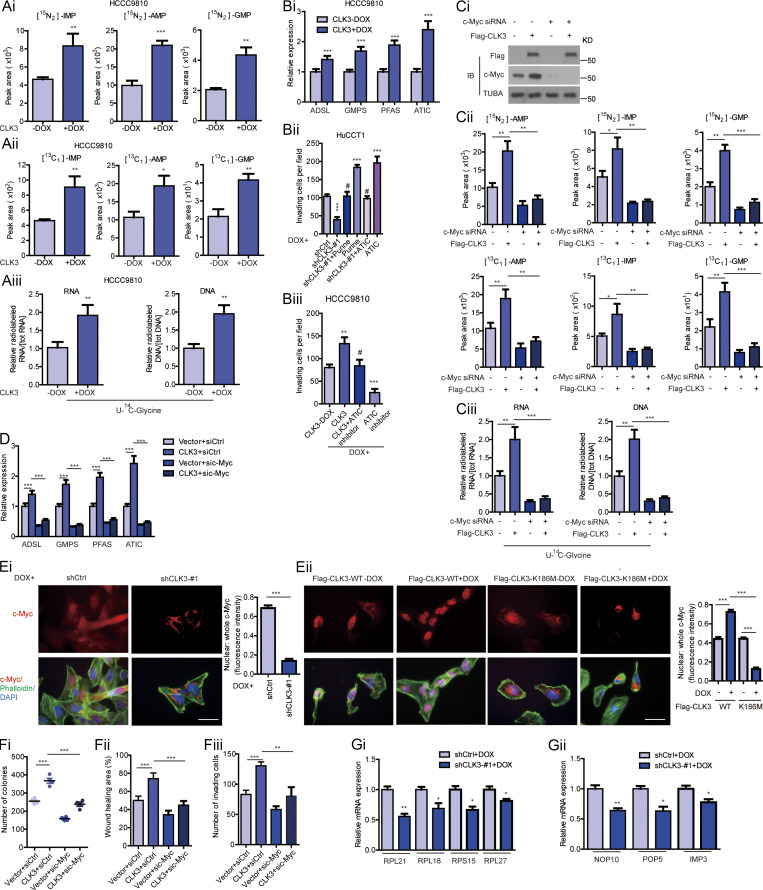
Figure S2.
CLK3 promotes purine synthesis and CCA progression through enhancing the stabilization and nuclear translocation of c-Myc. (Ai) LC-MS/MS analysis was performed to measure 15N-glutamine–labeled intermediates of purine synthesis in HCCC9810 cells with or without Dox-induced CLK3 overexpression. (Aii and Aiii) LC-MS/MS was used to analyze metabolites labeled with 13C-glycine (ii) and 14C-glycine (iii) in HCCC9810 cells with or without Dox-induced CLK3 overexpression. (Bi) Performing quantitative RT-PCR assays as indicated in HCCC9810 cells with or without Dox-induced CLK3 overexpression. (Bii) CLK3 silencing significantly decreased HuCCT1 cell invasion while overexpressing ATIC or adding purine markedly reverted this defect. (Biii) ATIC inhibitor significantly reverted the invasion of HCCC9810 cells induced by CLK3 overexpression. (Ci) Western blots confirmed CLK3 overexpression and c-Myc knockdown in HCCC9810 cells. (Cii) The effects of silencing c-Myc on the levels of GMP, AMP, and IMP in HCCC9810 cells with CLK3 overexpression. (Ciii) Silencing c-Myc reduced the levels of U-14C-glycine in HCCC9810 cells with CLK3 overexpression. (D) The knockdown of c-Myc suppressed purine-associated enzymes in HCCC9810 cells with CLK3 overexpression. (Ei and Eii) The impacts of CLK3 knockdown or overexpression on the nuclear translocation of c-Myc in HuCCT1 (i) or HCCC9810 (ii) cells were analyzed by immunofluorescence staining and were quantified. Bars, 50 µm. (F) Silencing c-Myc reverted the aggressiveness of HCCC9810 cells with CLK3 overexpression. (G) CLK3 knockdown reduced the mRNA levels of genes of ribosome components (i) and their regulators (ii). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; #, not significant. Data are mean ± SEM and are from three (A, B, Cii, Ciii, D, E, and Fii, and Fiii) and four (Fi) independent experiments or are representative of three independent experiments with similar results (Ci). P values were calculated using unpaired Student’s t test (Ai, Bi, and Ei) or one-way ANOVA (Bii, Biii, Cii, Ciii, D, Eii, and F). KD, knockdown; IB, immunoblot; AMP, adenosine monophosphate; GMP, guanosine monophosphate; IMP, inosine monophosphate; TUBA, alpha tubulin.