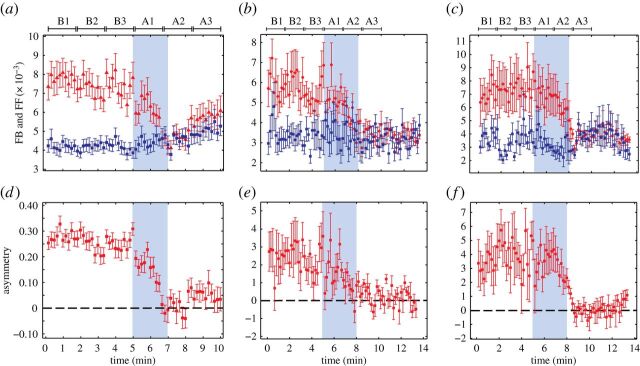
Figure 4.
A common neural correlate of anaesthetic-induced unconsciousness. The inhibition of asymmetry between the feedback (FB, red triangles) and feedforward (FF, blue squares) connectivity is a common feature found across three heterogeneous anaesthetics. The FB/FF connections (a–c) and their asymmetry (d–f) in the frontal–parietal network are shown for (a,d) ketamine (n=30), (b,e) propofol (n=9) and (c,f) sevoflurane (n=9). The means and standard errors are denoted in each window. Anaesthetic administration is highlighted with blue shade. Six substates (B1, B2, B3 in baseline state and A1, A2 and A3 in anaesthesia) for the statistical tests are denoted. Each substate consists of ten 10 s long EEG epochs; time scales differ between ketamine and propofol/sevoflurane because data were collected in different studies. (Courtesy of Lee et al. [29].)