FIGURE 2.
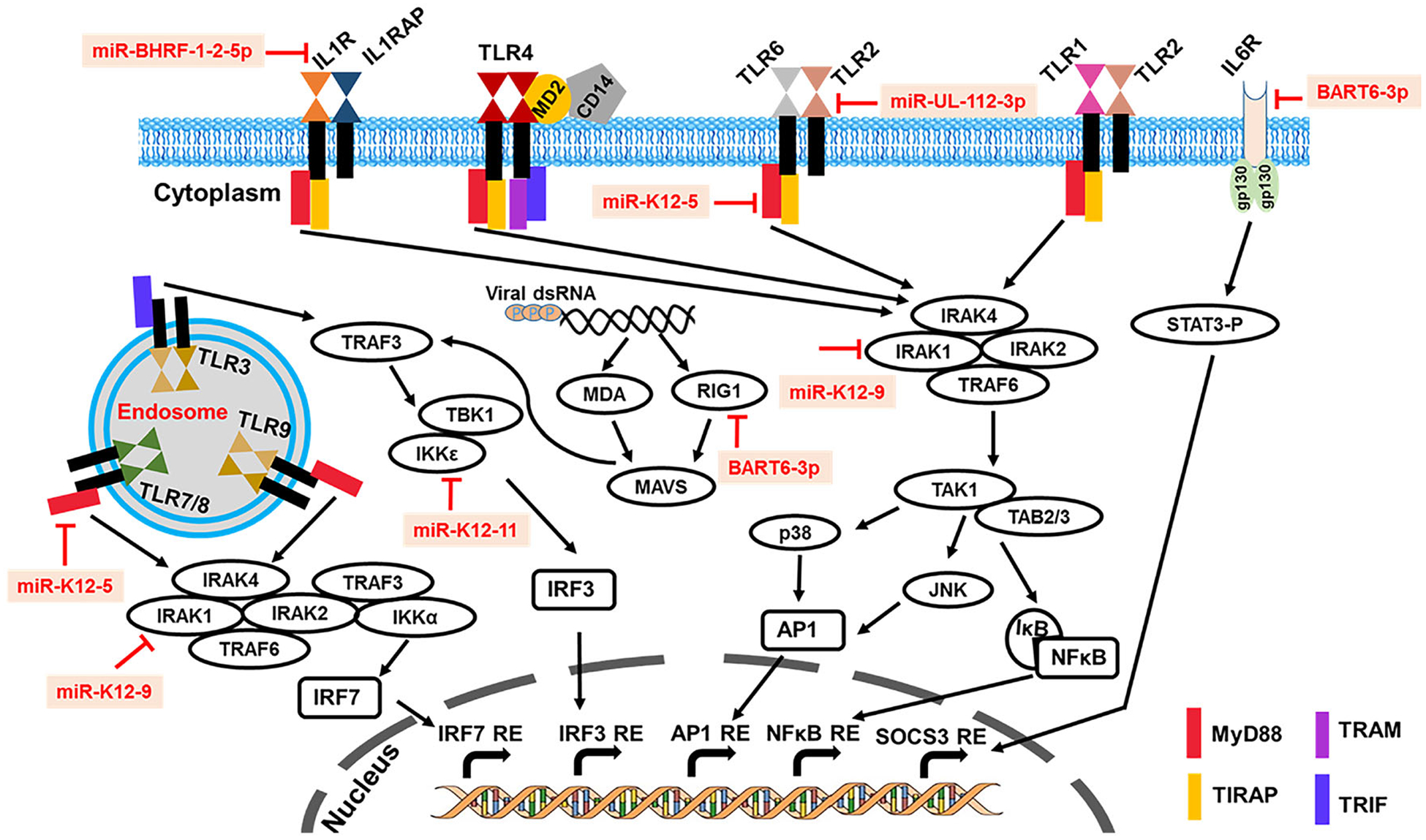
Overview of viral miR-mediated suppression of host innate immune pathways. The illustration summarizes known mechanisms by which individual viral miR interact with host genes involved in virus recognition and activation of innate immune responses. Viral miR promote immune evasion by directly targeting host genes involved in the recognition of virion, virus-derived nucleic acids (DNA/RNA) or proteins to suppress antiviral pathways. Viral miR have evolved to target, essentially, all of the known viral defense mechanisms by targeting one or more critical components of the innate immune pathway. Functions of selected validated herpesvirus-encoded miR and host innate immunity genes are highlighted in the schematic. Viral miR inhibit production of proinflammatory cytokines and interferons that are required for recruitment and activation of adaptive arm of immunity, which can elicit robust antiviral response to contain herpesvirus infection by clearing infected cells
