Fig. 1.
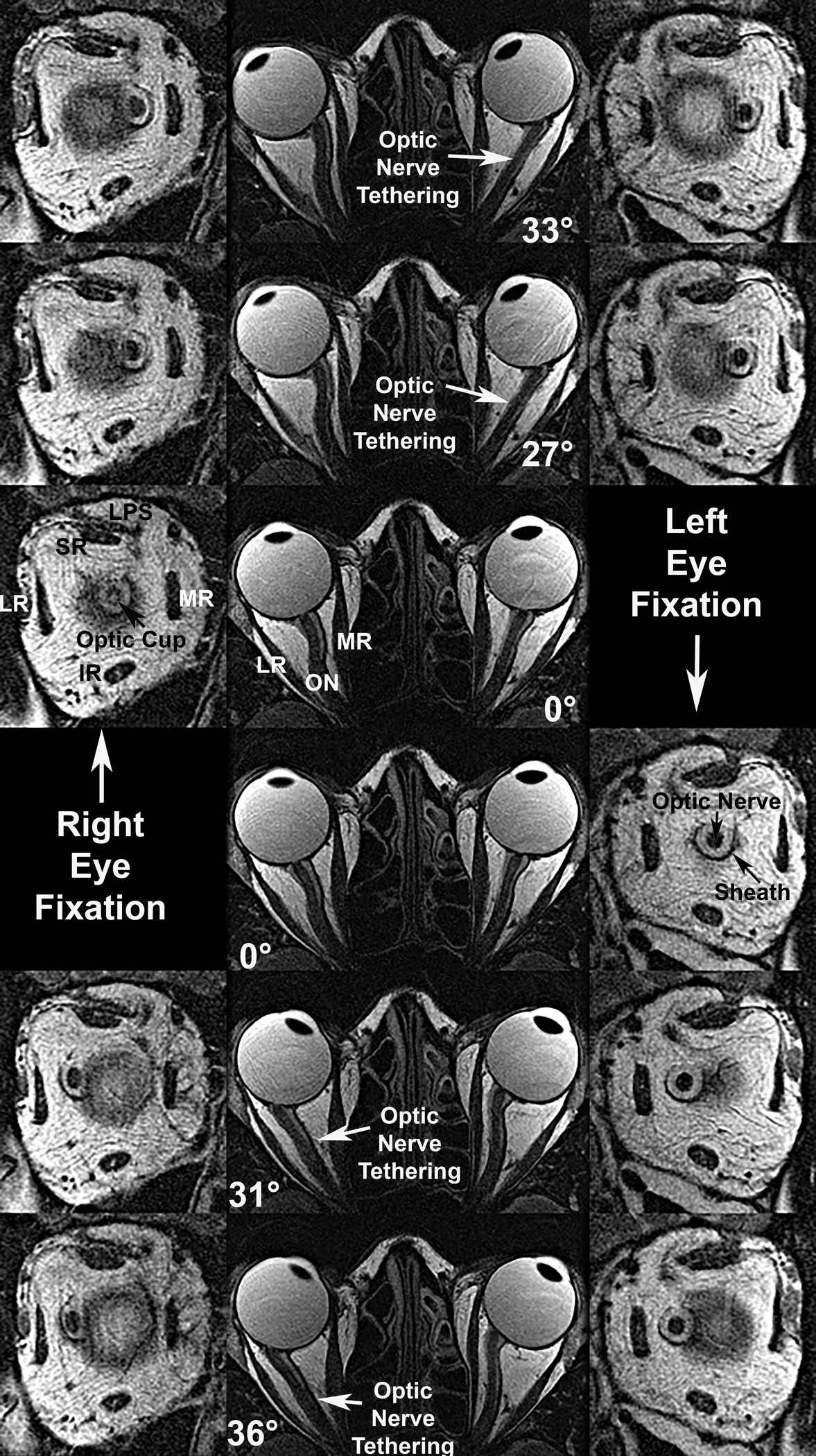
Axial (center column) and quasi-coronal (left and right right columns) MRI of both orbits in a patient with advanced OAG and maximal IOP exceeding 21 mmHg, imaged in maximal dextorversion (top row), moderate dextroversion (second row), central gaze (third and fourth rows), moderate levoversion (fifth row), and maximal levoversion (bottom row). Duction angles are listed. Each ON tethered in moderate adduction and remained so in maximal adduction, while being sinuous centrally and in abduction. Quasi-coronal just posterior to the globe-ON junction demonstrate that the ON within its sheath is surrounded by a white ring of cerebrospinal fluid. Both ON cross sections are subnormal due to glaucomatous atrophy, and an enlarged optic cup is evident in the right eye (third row, left). IR – inferior rectus muscle. LPS – levator palpebrae superioris muscle. LR – lateral rectus muscle. MR – medial rectus muscle. SR – superior rectus muscles.
