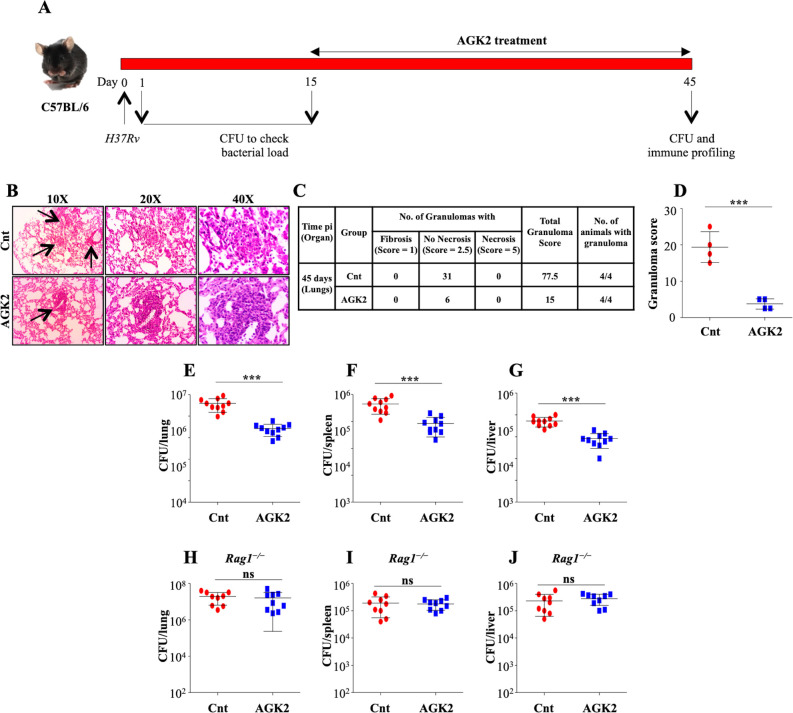
Figure 6. SIRT2 inhibition restricts mycobacterial growth in vivo.
(A) Schematic representation of the murine model of infection. A group of C57BL/6 mice were infected with low dose of H37Rv. After 15 days of disease establishment, mice were either left untreated or were treated with AGK2 (20 mg/kg) for 30 days. (B) Histopathological analysis of infected lungs with arrows indicating the granulomatous lesions. (C and D) Quantification of the number of granulomas (granuloma score) observed in the infected mice. (E–G) Bacterial load in the lungs, spleen and liver of mice at 45 days pi. (H–J) A group of Rag1-/- mice were infected with low dose of H37Rv followed by treatment with AGK2 (20 mg/kg) for 30 days. The graphs represent bacterial burden in the lungs, spleen and liver of Rag1-/- mice. E-J represents combined data from two independent experiments with four to five mice in each group. Granuloma score was obtained from the lungs of four mice per group. Data is represented as mean ± SD. *p<0.05, **p<0.005, ***p<0.0005.